Dutch journalist Gemma Venhuizen embarked on the MV Ortelius during the Weddell Sea cruise 'In search of the emperor penguins'. She had several encounters with this majestic penguin species - both from the sea and from the air.

Imagine yourself in a white, frozen world. No trees, no buildings - not even sunlight during the Antarctic winter months. Only the moon and the stars break the darkness of the polar night. Welcome to the realm of the emperor penguin. Standing up to 1.23 meters tall and weighing up to 40 kilograms, the emperor penguin is much larger than chinstrap, gentoo, Adélie, and other penguin species. Its plumage enhances its regal appearance: the classic black and white tuxedo is complemented by a colorful tie - a beautiful orange-yellowish hue on its throat.
Kneeling for the Emperor
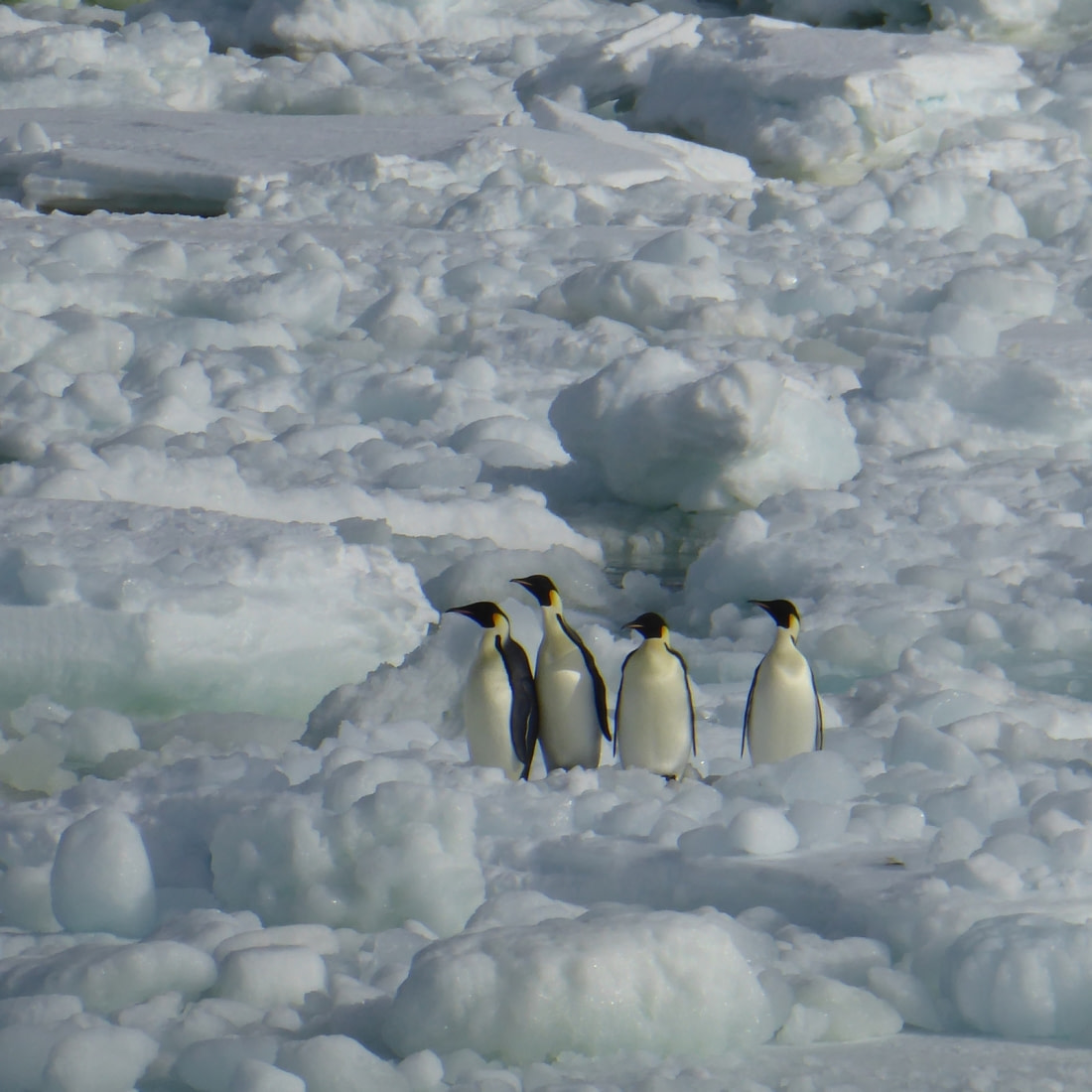
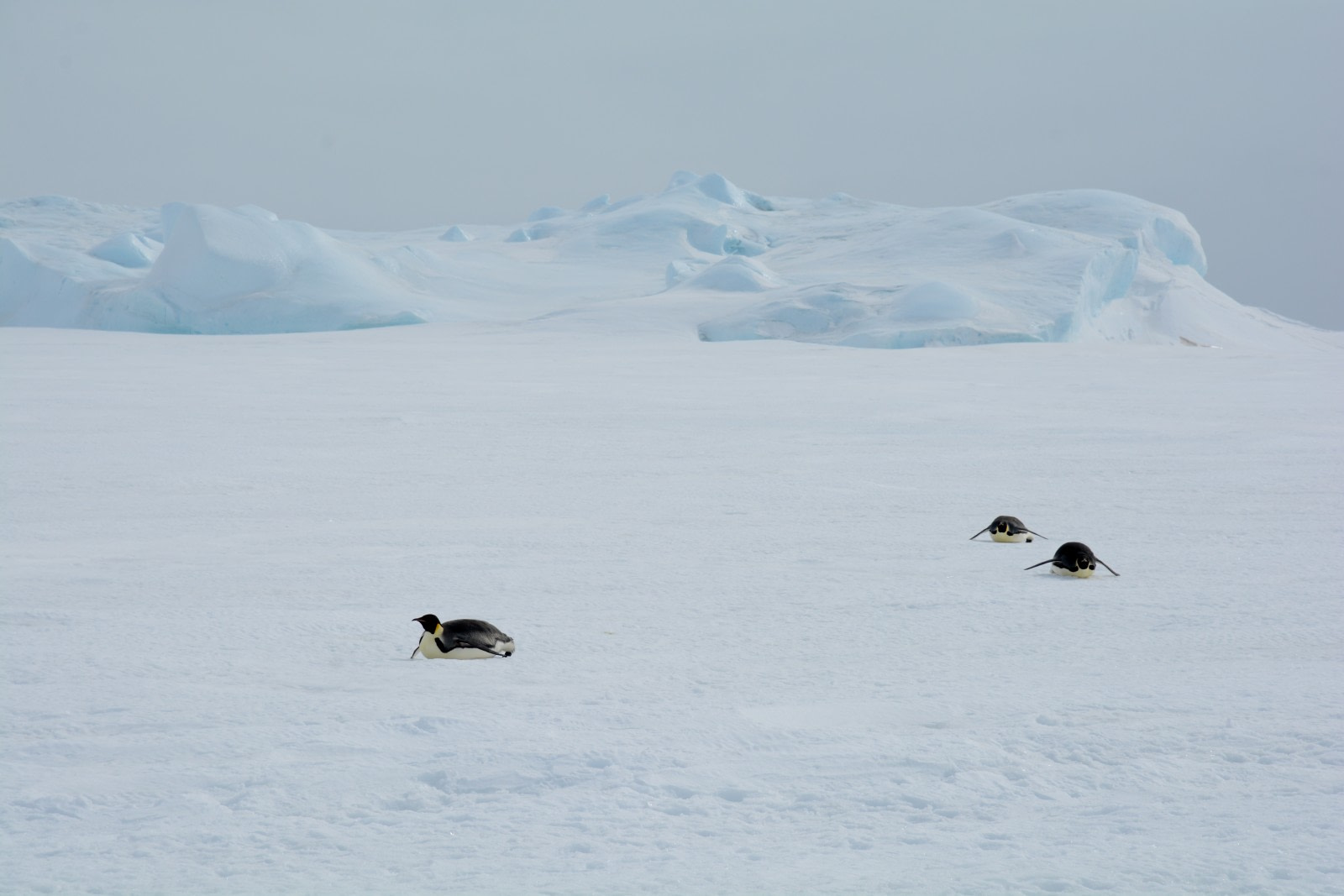
The first time I found myself face to face with an emperor penguin was during a trip at the break of Antarctic summer - December 1st, also known as International Antarctica Day. We had just embarked on the Zodiacs for a small cruise. The Ortelius was towering above us.
As we approached the ice edge, we noticed a solitary figure standing solemn and upright. I heard the sound of camera shutters and bag zippers as people around me reached for their binoculars and long-focus lenses. I had neither, so I just stared - almost feeling like a voyeur. The emperor seemed to stare back, and I crouched a bit: kneeling, as far as possible in a small rubber boat, seemed the only logical thing to do.
True Antarctic Species
Of the seventeen penguin species around the world, only two are 'true' Antarctic ones: the Adélies and the emperor penguins, which live and breed on the Antarctic continent. Some other species - gentoo, chinstrap, and macaroni penguins - breed on the northern tip of the Antarctic peninsula, but they don't venture as far south as the emperors and Adélies do. Moreover, emperor penguins are the only penguins that breed during winter on the sea ice. Therefore, climate change poses a significant threat to them. A WWF study from 2008 estimated that approximately 50 percent of the emperor penguins will disappear if the global average temperature rises by 2 degrees Celsius - yet another reason to combat global warming.
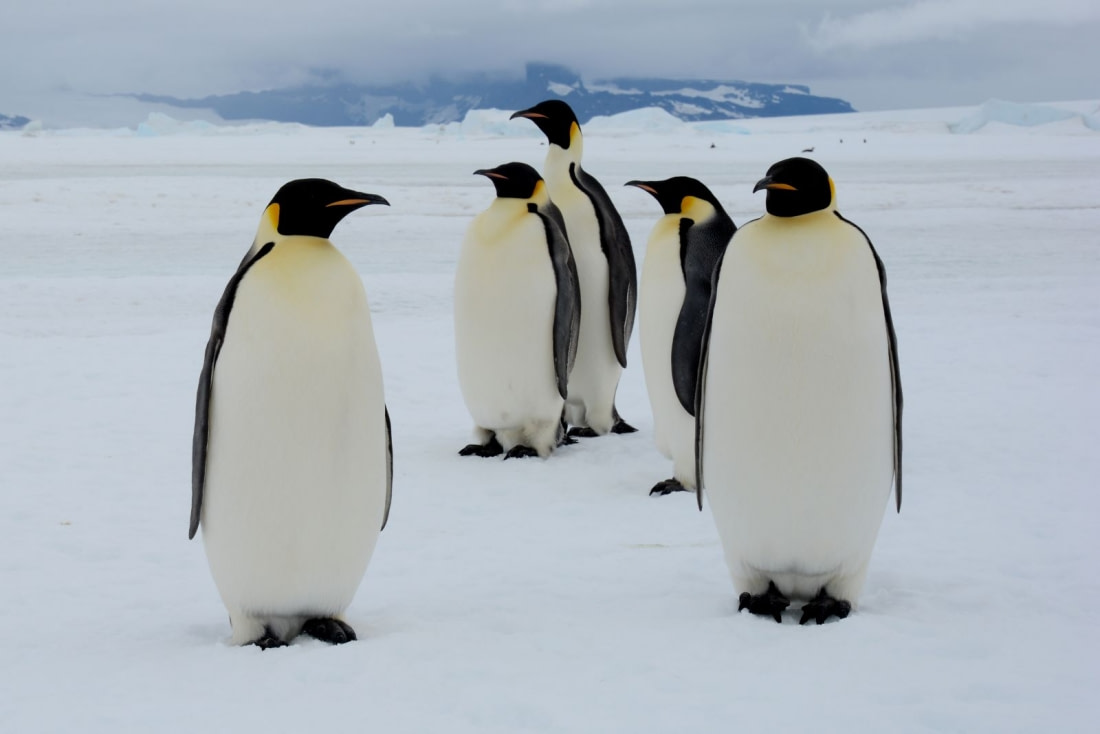

Fluffy Chicks
As I crouched in the zodiac, only meters away from this unique bird, I knew there was a penguin crèche nearby. A few kilometers from us, at this exact moment, there would be a hustle and bustle of thousands of grown-up emperors and fluffy chicks. Flapping, stumbling, and squealing their way around the colony - the real-life version of the movie Happy Feet. Not knowing what their parents had to endure during the previous months. I thought of another movie I had seen before my visit to the Antarctic: March of the Penguins, about the epic journey that emperor parents undertake to care for their unborn child. Emperor penguins are the least common Antarctic penguin: there are only around 200,000 breeding pairs.
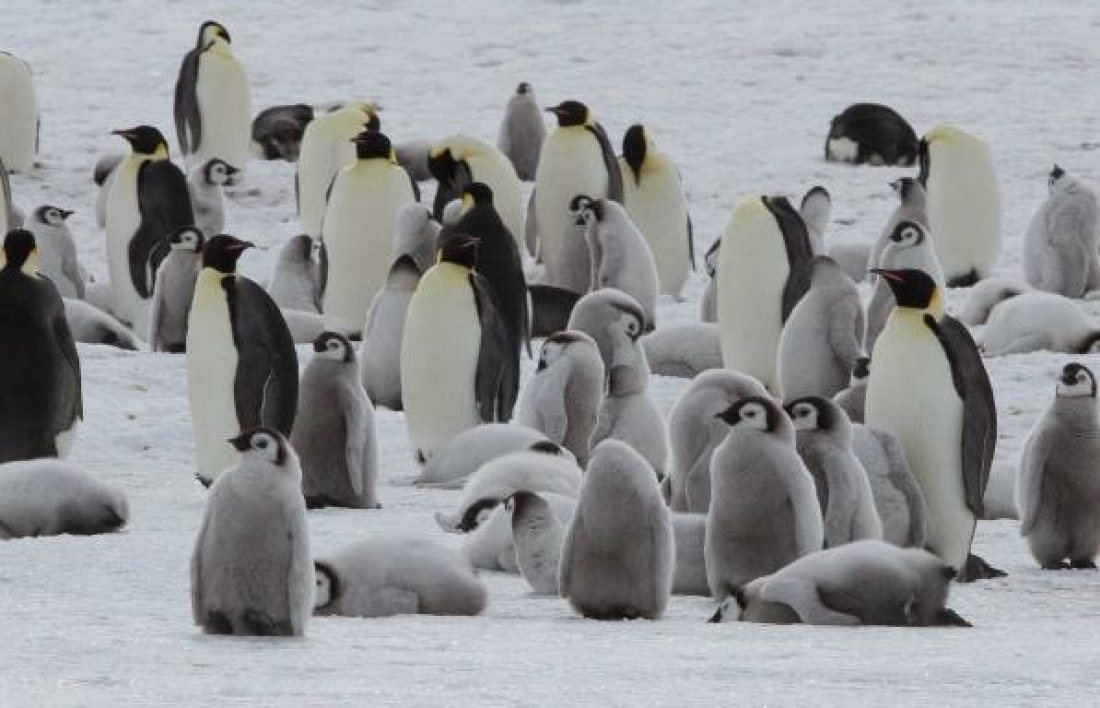

-60 Degrees Celsius
In May, at the beginning of the Antarctic winter, the female lays a single egg. She then passes it over to her partner, who will incubate it for nine weeks during the coldest time of the year. Temperatures might reach -60 degrees Celsius, accompanied by wind gusts over 180 km/hour. The female will march over 100 kilometers to the ice edge, where she can fill her stomach with crustaceans, squid, and small fish. Emperors can dive deeper and longer than any other bird: they can dive over 200 meters deep for a period of 18 minutes. During this period, the male fasts; his body weight is reduced by almost 50 percent. When the female returns, it's time for the male to go on his quest for food.
All this time, the egg is kept warm by the parent that is on duty. The penguins cover the egg with their body to shield it from the cold. The egg is lying on their feet. According to the website of the British Antarctic Survey, the egg can be 70°C warmer than the outside temperature, due to the thick layer of skin and the dense feathers - about 280 feathers per square centimeter.
Helicopter Flight
No matter how impressive the march of the emperor penguins is, it still looks a bit clumsy: a wiggling penguin is adorable. The emperor penguin that we encountered during our zodiac cruise, however, chose another way of transport. We saw him sliding on his belly towards the ice edge - and that surely was an impressive sight. He used his wings as paddles and his feet as an 'engine'. This way of transportation was very effective: in no time, he disappeared from sight. Meanwhile, our zodiac was surrounded by drift ice, and we had to return to the Ortelius immediately to prevent getting stuck in the ice. Back on board, the crew had a surprise for us: we would make a helicopter flight over the nearby emperor penguin colony at Snow Hill Island.
Hopefully, there won't be too many skuas around in the colony. They are the mortal enemies of emperor penguin chicks. Penguin parents who lose their child sometimes kidnap a chick from a neighboring couple. Fortunately, the survival rate of emperor penguins is high: 95 percent survive the first year. Unless the sea ice conditions are harsh: in that case, many chicks starve to death. Many emperor penguins wait to mate until they are 6 years old. They can live up to 20 years.

Black and Gray Dots
We split up into several groups: there were two helicopters on board, one for 4 passengers, one for 5 passengers. Inside, it was cozy and noisy - luckily, we had ear protectors on. The Chilean pilot smiled at us, and then we took off. I was enjoying the scenery so much that I almost forgot the purpose of the trip. Then, however, one of my friends pointed at thousands of black specs beneath us. This time, I was better prepared than in the Zodiac: I had my binoculars with me. And indeed, right below the helicopter was a huge colony of emperor penguins. I could even see smaller gray dots: the emperor chicks. I was cheering so loud that my fellow passengers could hear it, even with their ear protection on.





Related Trips
Blog



Imperial Antarctica: the Snow Hill Emperor Penguins
First to the North Pole: Five Failed but Brave Expeditions

Arctic on Foot: Hiking and Snowshoeing the Far North

Six Facts About the Crabeater Seals of Antarctica

Shackleton’s Push to the South Pole

What’s so Special about East Spitsbergen?

The Northern Lights dancing across the skies

The Impact of Small vs. Large Cruise Ships

Port Pastimes: 7 Fun Things to Do in Longyearbyen

Visiting the Nearly Unknown: New Zealand’s Campbell Island

Living the Antarctic Dream

Five Reasons to Love St. Helena

Ice streams and lakes under the Greenland Ice Sheet

Greenland's History: When Vikings Ruled the Ice Age

8 Scientific Wonders of the Arctic

Adding Antarctica to Your Seven-Continents Bucket List

10 Common Misconceptions About the Arctic

The Ice-Jewelled Geology of Spitsbergen

Path of Polar Heroes: Hiking Shackleton’s Historic Route






 28 Days / 27 Nights
28 Days / 27 Nights




