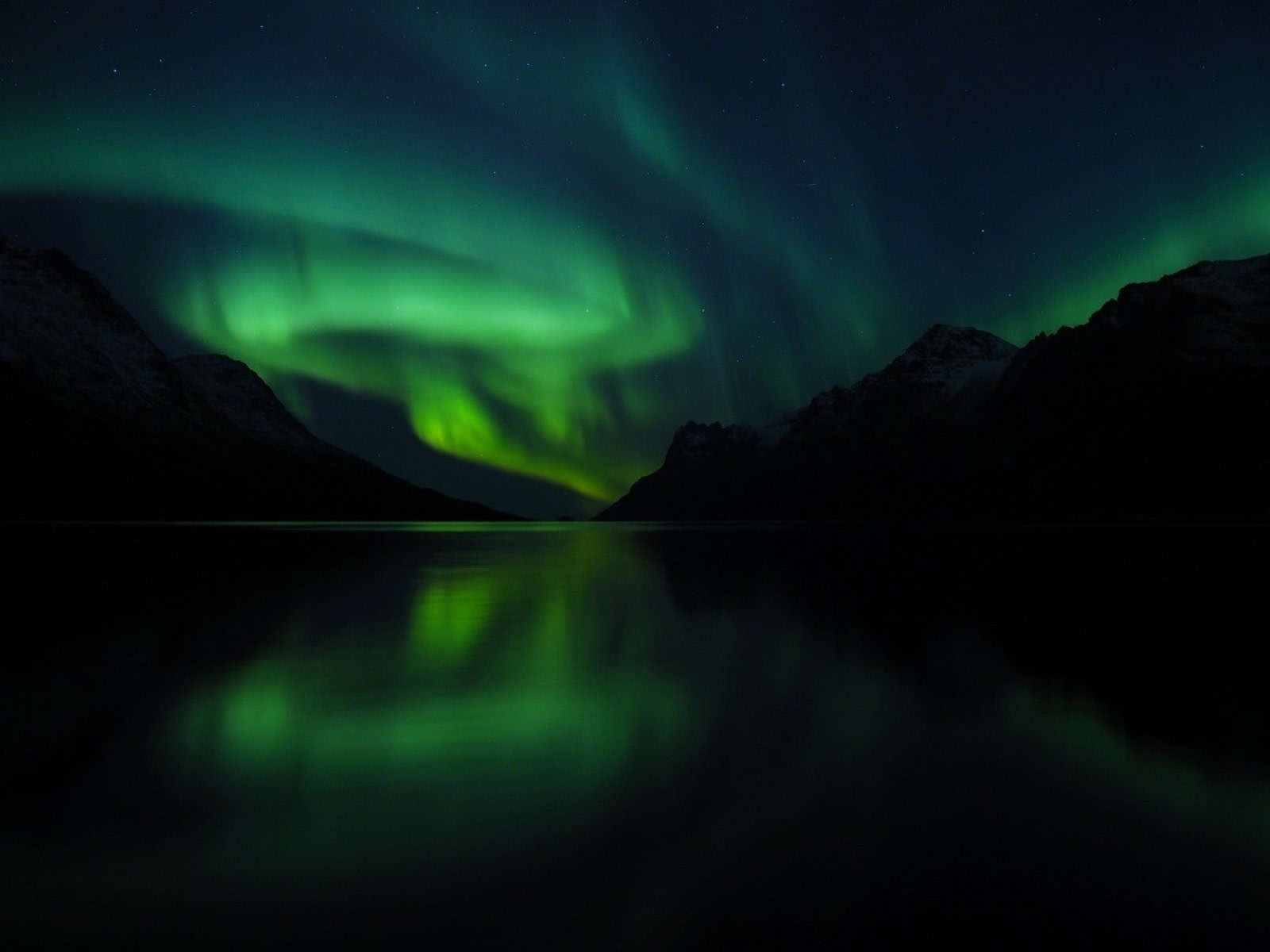
In Roman mythology, Aurora was the goddess of the dawn. The term "borealis" is derived from the Greek word for "wind." Thus, "aurora borealis" translates to "dawn wind," commonly known as the Northern Lights. This natural phenomenon has captivated humanity for millennia and remains a major attraction in the Arctic, with numerous cruises dedicated to witnessing this mesmerizing light display.
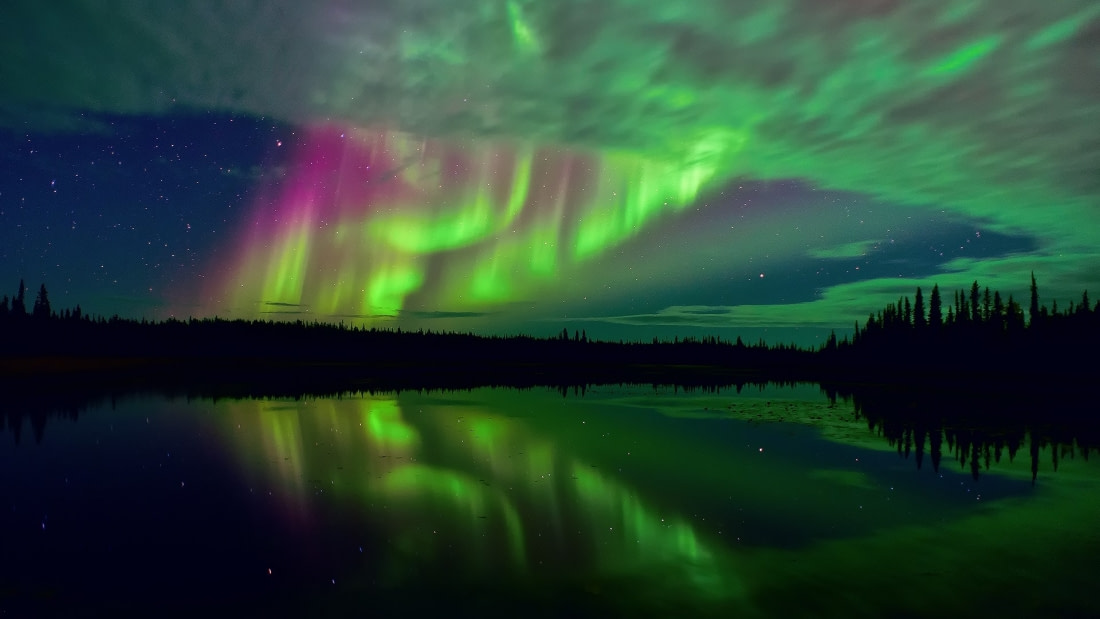

1. The Ancients Thought the Northern Lights Were Fire
For thousands of years, the origin of the Northern Lights was a mystery. Aristotle provided the first scientific account in the 4th century BCE, comparing them to flames of burning gas. In the 13th century CE, the Norwegian text Konungs skuggsjá, or The King’s Mirror, offered a detailed explanation, suggesting the lights were reflections from Earth’s oceans or sunlight from below the horizon. Some even speculated that fires in Greenland caused these mysterious lights.
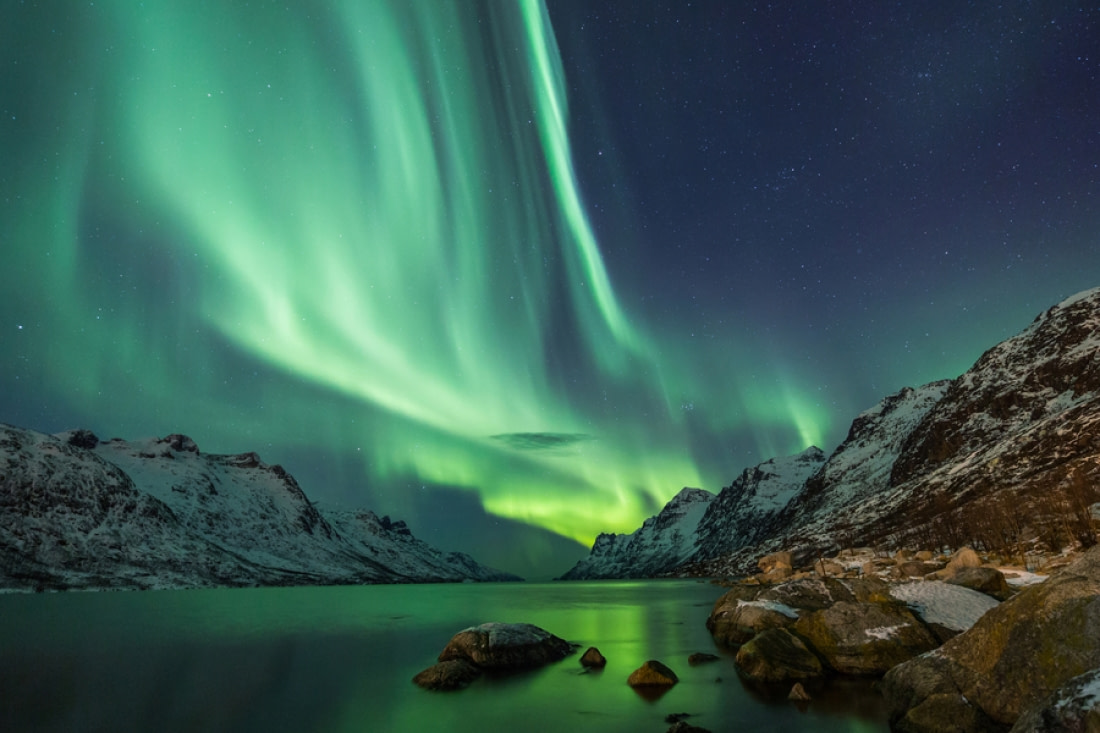

2. An Aurora in Europe Sparked Aurora Borealis Insights
In 1708, Swedish scientist Sun Arnelius proposed that solar rays were reflected off ice particles into the atmosphere. Eight years later, a strong aurora in Europe prompted further scientific investigation. Sir Edmund Halley published a detailed description, suggesting that auroral rays were due to particles influenced by Earth's magnetic field.
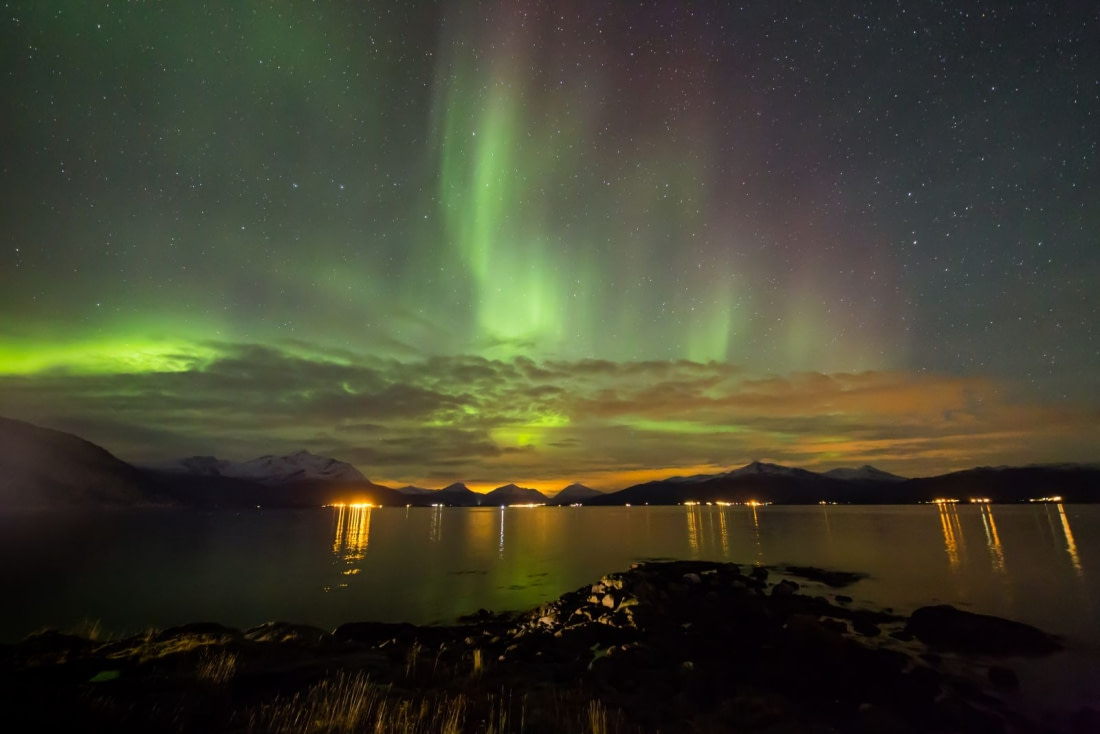

3. The Northern Lights Continuously Encircle the North Pole
In the 1800s, Christopher Hansteen established observation stations and collaborated with sea captains to record Earth's magnetic field. He was the first to note that the aurora forms a continuous ring around the geomagnetic pole. Danish astrophysicist Sophus Tromholt further confirmed this by organizing a network of observation sites, discovering that the lights indeed form a ring around the North Pole.
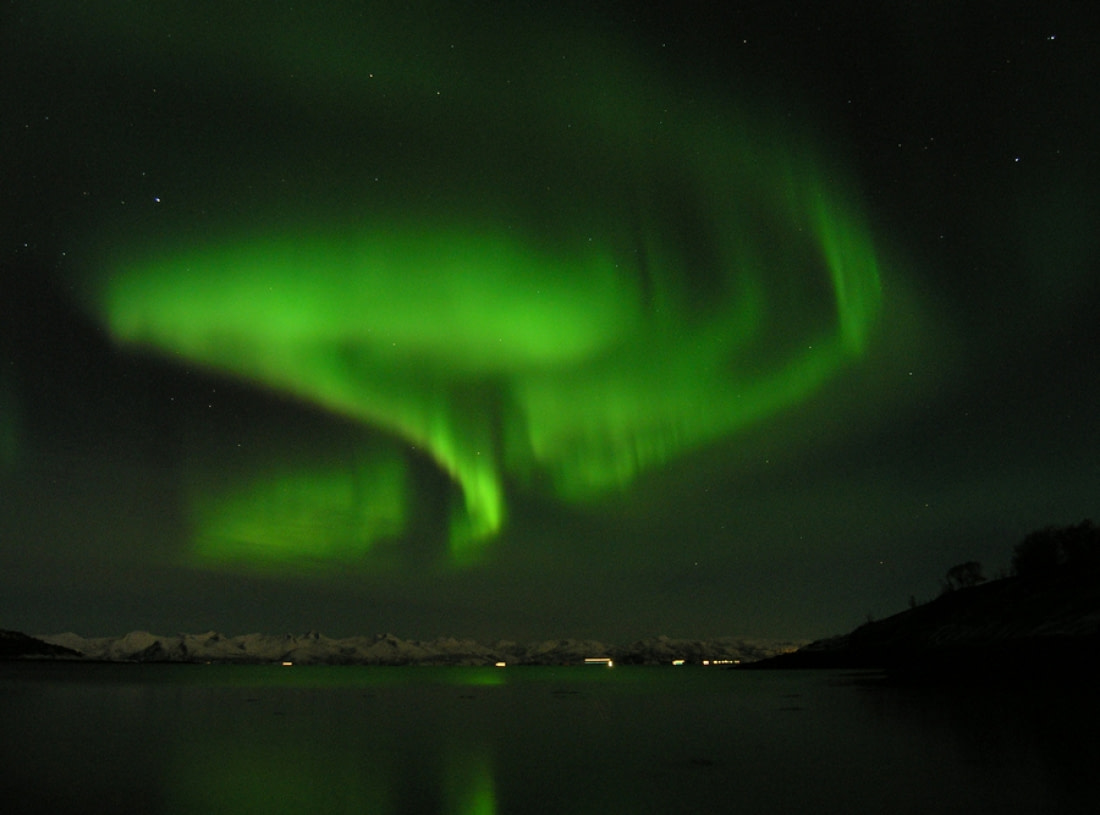

4. Earth’s Magnetic Field Guides the Northern Lights
In the early 20th century, Norwegian physicist Kristian Birkeland conducted an experiment with a spherical magnet in a vacuum chamber, shooting an electron beam at it. He found that the beam was guided by the magnetic field, hitting the sphere near the poles. Birkeland concluded that the sun must be firing beams toward Earth, guided by Earth's magnetic field near the poles.
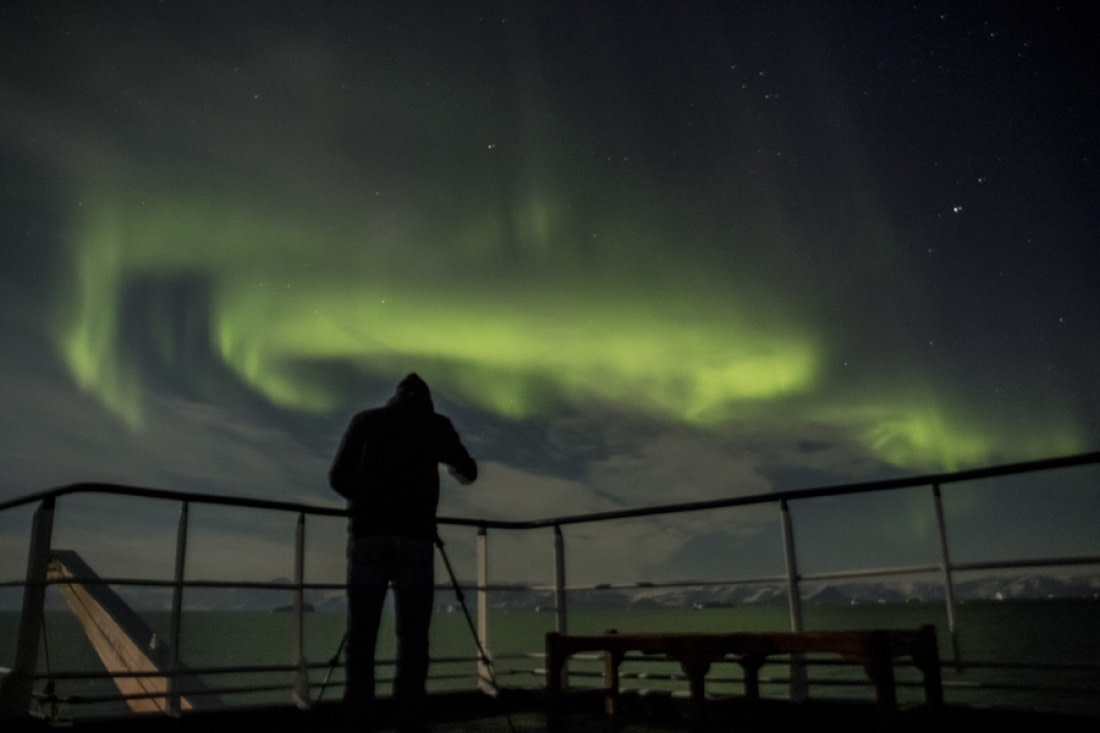

5. Trapped High-Energy Solar Particles Make Up the Aurora Borealis
In the 1930s, Sydney Chapman and Vincent Ferraro hypothesized that clouds of electrically charged particles from the sun envelop Earth. Research showed that as these particles reach Earth, most fly past, while some swirl back and enter the atmosphere. Satellite data from the Space Age revealed that space around Earth is filled with high-energy particles trapped by Earth's magnetic field, along with solar wind, enabling scientists to map the magnetosphere.
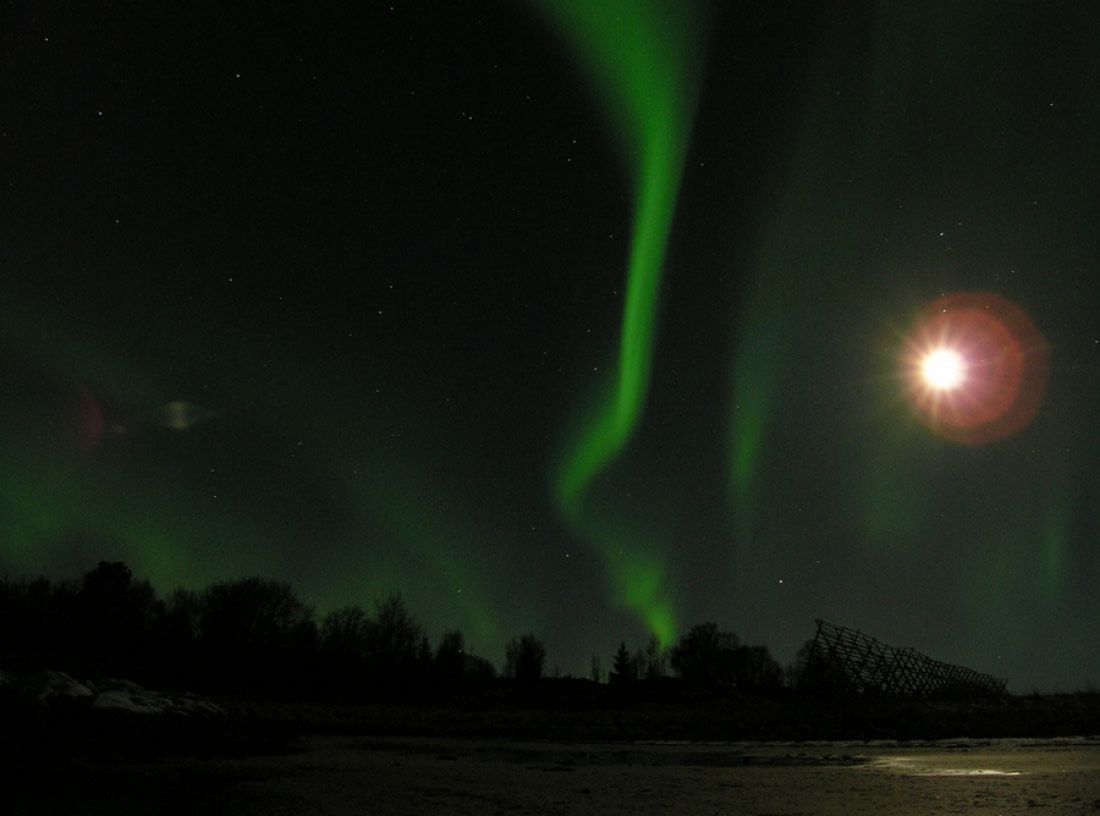

6. Northern Lights Solar Particles Move Millions of Miles Per Hour
Today, we understand that the Northern Lights are created by solar flares shooting through space from the sun. These flares result from collisions between gas molecules on the sun's surface, releasing large quantities of matter and electromagnetic radiation. Traveling at around seven million miles per hour (11,265,408 kph), these flares take one to five days to reach Earth, depending on the solar wind's speed. As they reach Earth's atmosphere, most particles continue past Earth, but some enter the atmosphere above the magnetic poles.
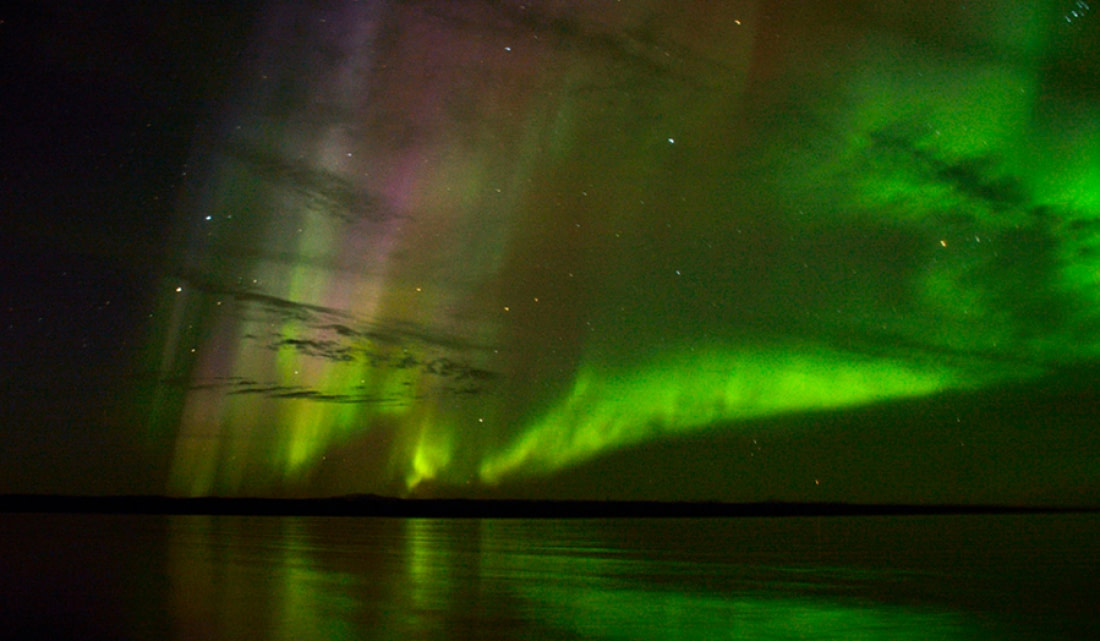

7. The Northern Lights Are Diffuse (Soft) or Discreet (Sharp)
Most auroras occur in a band called the auroral zone, located 3 to 6 degrees latitude from the geographical poles. The Northern Lights can be either diffuse or discrete: Diffuse auroras form a featureless glow that may not be visible to the naked eye, while discrete auroras have sharp features and can vary significantly in brightness.
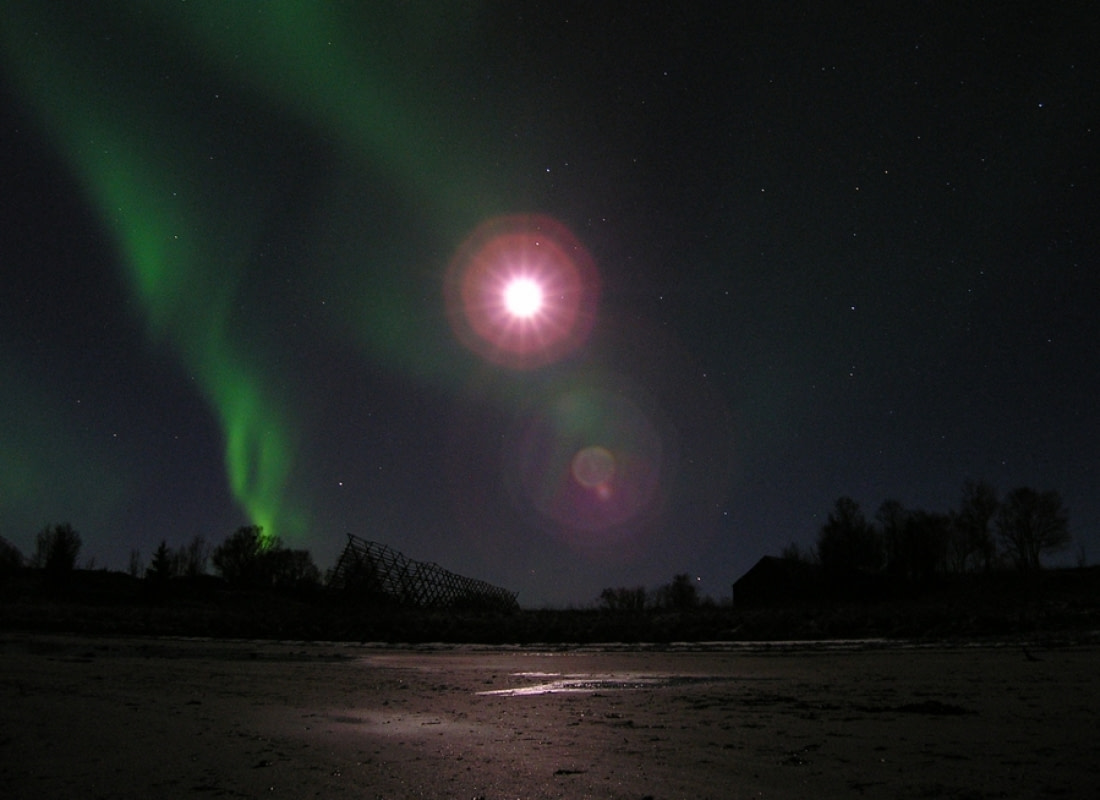

8. Auroral Breakups Bring the Northern Lights to Life
The most spectacular part of watching the Northern Lights is witnessing an auroral breakup. This event involves a brightening of forms and rapid changes in the aurora, transforming from plain to rayed before swirling and dancing in the sky. Multiple breakups can occur on a single night of moderate to high activity, while a low-activity night may have one or two breakups.
Scientists advise viewers to stay put if they see multiple bands appearing in an area, as this indicates a likely breakup. If these bands appear early in the evening, the breakup will likely be spectacular, with many more to follow. After a big breakup, there may be no activity for half an hour to an hour, and breakups themselves can last around that long.
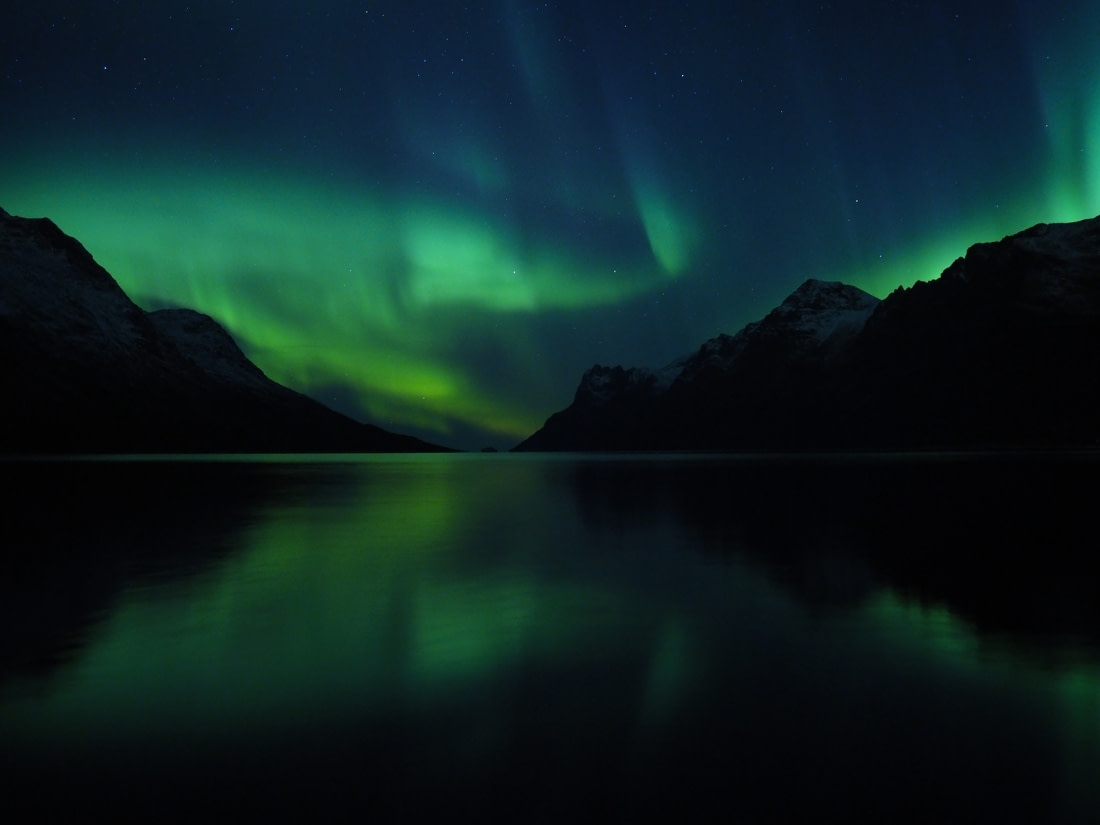

9. Aurora Borealis Colors Come from Gas and Electrons
The colors of the Northern Lights depend on gas and electrons in the atmosphere. High-energy electrons cause oxygen to emit green light, while low-energy electrons cause red light. Nitrogen typically gives off a violet or pink color, while vertical blues result from electrons colliding with ionized nitrogen.
Altitude also affects color formation. At high altitudes (over 105 miles, 170 km), reds are generated; at middle altitudes (60 – 105 miles, 95 – 170 km), green is generated; and at lower altitudes (50 – 60 miles, 80 – 95 km), pink and violet are generated. Large solar storms can cause red to appear at lower altitudes.
The color variations occur because oxygen takes around a second to emit green light and up to two minutes to emit red light. Higher altitudes contain more atomic nitrogen, allowing atoms time to emit red, while pinkish colors result from the combination of red from oxygen and blue from nitrogen.
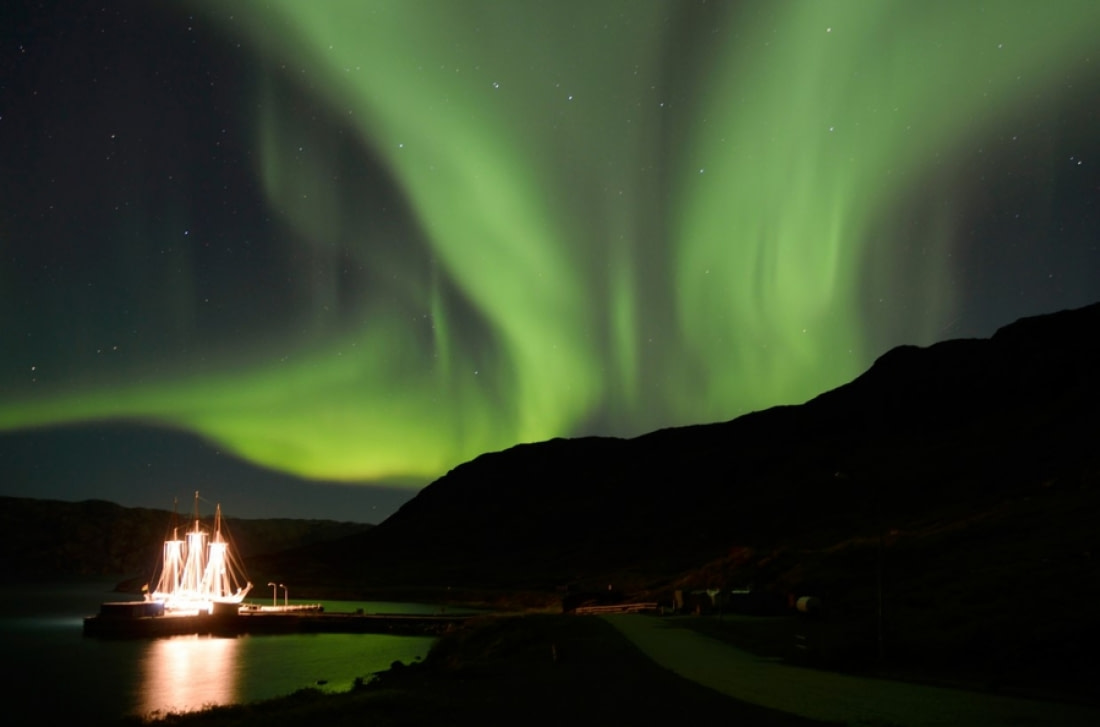

10. Practice Makes Perfect Northern Lights Pics
To capture the perfect photo of the Northern Lights, first check the weather and visit a website for aurora forecasts. A clear sky free of light pollution is crucial, and some photographers prefer the moon for natural foreground lighting. Proximity to water can also provide stunning reflections of the aurora.
For this type of photography, a wide-angle zoom lens is recommended. With exposure times usually ranging from 20 to 30 seconds, securing your camera to a tripod is essential. Avoid breathing out in awe while looking through the viewfinder, as this can fog the lens and leave condensation that might later freeze. This may take some practice, but the results will be worth it.
Blog



Light in the Land of the Midnight Sun

12 Things to Do in Antarctica

10 Weather-Fueled Facts about Antarctica

Where the Polar Bears Roam

Exploration of the Polar Regions

Penguins, Petrels, and Prions: Top Antarctica Bird Tour Spots

Birds of the South: 33 Antarctic Birds and Seabirds

12 Tips to Help Keep Birds Safe During an Antarctic Cruise

The Ancient Fossil Forests of Antarctica

The first race to the South Pole in 50 years

The Wildlife of Antarctica’s Seas and Skies

Arctic on Foot: Hiking and Snowshoeing the Far North

Visa to Argentina for Antarctic Expedition Travelers (2025 Guide)

Narwhals: the Aquatic Unicorns of the Arctic
The ozone layer in Antarctica

Shackleton’s Long-Lost Endurance Discovered in Antarctica

The Enchanting Islands of Svalbard

What to Expect When Crossing the Drake Passage

Why a Polar Diving Cruise Should be Your Next Great Decision






