An Antarctic cruise may explore the upper tip of the Antarctic Peninsula where one finds Graham Land, a jagged, glaciated part of Antarctica with a landscape dominated by volcanoes. Despite the volcanoes being over 200 million years old they are far from extinct with volcanic activity occurring today. Graham Land is connected to Palmer Land at the point where the Antarctic Peninsula widens from around 75 km to around 200 km south of Marguerite Bay.
Subduction in Graham Land
Volcanoes in Graham Land are formed above a subduction zone where tectonic plates converge and one plate subducts below another. In Graham Island the Phoenix tectonic plate, which has from the Cretaceous times has underlayed a large part of the eastern Pacific subducted to the east beneath Graham Land.
Molten magma rose to the surface in pipes and erupted to form a chain of volcanoes. Subduction gradually died out in most of Graham Land but is still continuing at a slow rate beneath the South Shetland Islands. Remnants of volcanic activity nonetheless can be seen as the deep submarine trough to the northwest of the islands is where the Phoenix plate is still subducting.
Rocks from the supercontinent Gondwanaland
The earliest rocks found on Graham Island date back to when Antarctica was part of the supercontinent Gondwanaland, which consisted of South America, Africa, India, Australia and New Zealand. This continent existed over 500 million years ago until it broke up in the Jurassic period 180 million years ago.
Along Graham Land’s eastern coastline a few rocks exposed date back to this period. The oldest of the rocks exposed is from the Ordovician period 486 million year ago as well as rocks from the Devonian period 416 million years ago. The rocks are tough, hard and resistant to erosion as they are all granites and gneisses formed at the edge of Gondwana that today form the rugged, jagged ridges in the Scar Inlet and Joerg Peninsula along eastern Graham Land.
A more common type of rock found in Graham Land is a group of Carboniferous to Triassic sedimentary rocks called the Trinity Peninsula Group. This group of rocks was laid down in the seas around the Pacific Ocean edge of Gondwanaland. The sedimentary rocks were then folded by tectonic events on the continental margin and now form ‘’dark coloured, craggy hills and cliffs covering much of the North-eastern part of Graham Land’’.
Volcanic origins Graham Land rocks
Most of the rocks along Graham Land are from a linear belt of extinct volcanoes that ran along the current coastal mountains. These volcanoes were part of the ‘ring of fire’, a ring of volcanoes that surround the edges of the Pacific Ocean today. Volcanic activity started in Graham Land around 183 million years ago in the Jurassic period with large volumes of lava and volcanic ash forming volcanic deposits several kilometres thick. This was at the same time the supercontinent started to break up with Antarctica rifting away from the other continents.
Jurassic rocks
The Jurassic period volcanoes are mainly on the eastern side of Graham Land where they erupted as silica-rich volcanic ash deposits covering older volcanoes. Volcanic activity then moved westward with most of the volcanic rocks along the western part of Graham Land dating from around 146 million years ago to the present. Some of the volcanic rocks are hard and resistant to weathering, forming near vertical cliffs, while others are soft and weather to scree-covered slopes. Magma from the volcanic events along the western part of Graham Land has formed hard, crystalline granites that are commonly seen today along the coast as light grey rocks. Amongst the granites are dykes that channelled molten magma to the surface.
Graham Land an extension of the Andes
When looking at the map of Graham Land it would appear that it should be a continuation of the Andes mountain range and geologists have found evidence that it indeed is the case. Research has shown that Graham Land was joined to Patagonia until the two broke apart as the Drake Passage seaway opened up 30 million years ago. Scientists have found Jurassic volcanic ash deposits from on the eastern side of Graham Land also occur on the east of the Andes in Patagonia.
Graham Land volcanic activity today
Volcanic activity in Graham Land is still present however it is restricted to a volcanic rift in the Bransfield Strait. This strait formed when the South Shetland Islands separated from the western part of Graham Land around 4 million years ago, drifting northwest. A sea-flood map of Bransfield Strait shows an active volcanic rift along the sea floor. There are three dormant volcanoes along the sea floor – The Axe, Three Sisters and Orca – that is around 600 m above the sea floor. Both the Axe and Orca have a summit crater about 2 km across. Deception Island is the southernmost volcano that lies along the rift.
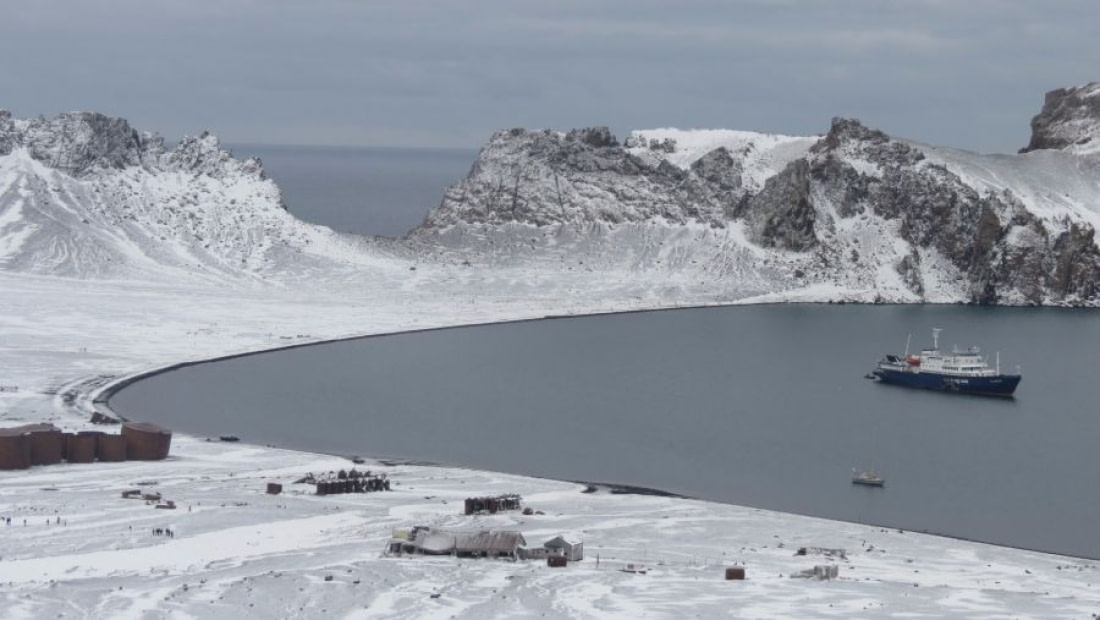
Deception Island one large volcano
Deception Island is the most recent active volcanoes in the Antarctic Peninsula. Located south of South Shetland Islands the island contains an 8 km wide volcanic crater flooded by the sea that now forms a central lagoon: Port Foster. The lagoon is reached through a small channel named Neptunes Bellows by whalers after the strong gusts that can ‘blast’ through the channel.
The volcano most recently erupted in 1967, 1968 and 1970 producing powerful explosions, dense ash clouds of black basalt cinders and ash. Mudflows also occurred from a mixing of ash and melted glacier ice. Scientists have found there are hot springs fed by water heated within the volcano, providing evidence that Deception Island is still underlain by hot molten rock. Data shows the volcano erupts a few times per century with the next one likely in the near future.

Fossilised life in Antarctica
When Graham Land’s volcanoes were active ash and sediments covered the surface plant and animal life was preserved, giving us a rich fossil record, enabling researchers to build a picture of the climate and environment in the past. Over the late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous period (160-100 million years ago) sediments of the Fossil Bluff Group on Alexander Island contain some of the most abundant and diverse fossil material on the Antarctic Peninsula.
Most of the fossils are marine bivalves, ammonites and sea urchins along with some starfish. In the South Shetland Islands the main fossils are of bivalve shellfish fauna. Sediments laid down behind the volcanic arc are exposed today revealing fossilised plants. Plant fossils include fossil wood, pollen, spores and leaf impressions. Scientists have identified a variety of fossil plants in the sediments including pine, cycads and gingko trees as well as ferns and mosses.
A warm Antarctica
It is shown from the sedimentary records that extensive forests similar to those in New Zealand and southern South America today were able to grow on Graham Land where ice now covers the landscape. This was due to the climate being much warmed that today despite it being at a similar latitude.
Temperatures were even warm enough during the Jurassic and Cretaceous period for plant and meat-eating dinosaurs to live in Antarctica with dinosaur species found in sediments in James Ross, Seymour and Vega islands. Vertebrate fossils were even found containing marsupials and several types of extinct penguins.
However, the climate cooled over 41 million years ago and by 34 million years ago large ice sheets started appearing in Antarctica. This lead to glaciation along Graham Land resulting in the fjords and jagged mountain ranges seen today.





Related Trips
Blog



True South: A New Flag for a Global Antarctica

Birds of the North: 29 Arctic Birds and Seabirds

Polar Bears and Pack Ice: 22 Pics from North Spitsbergen

Antarctica’s first Marine Protected Area

South Georgia Whaling Stations

Exploration of the Polar Regions

Antarctic krill: Antarctica's Superfood

Six Seal Species You Might See On Your Greenland Cruise

Eight Engaging Reindeer Facts

The South Georgia Seven: Hikes, Fjords, Whales, & Penguins

Arctic vs. Antarctica: A Traveler’s Guide

An igneous paradise: Franklin Island

Antarctic Icon: 44 Facts About the Emperor Penguin

Life in the Polar Regions

Svalbard’s 12 Most Iconic Animals

Life in a Penguin Colony

Not Eskimos: 10 Enlightening Facts About the Inuit

Circumnavigating Spitsbergen

Orcas of the Polar Seas




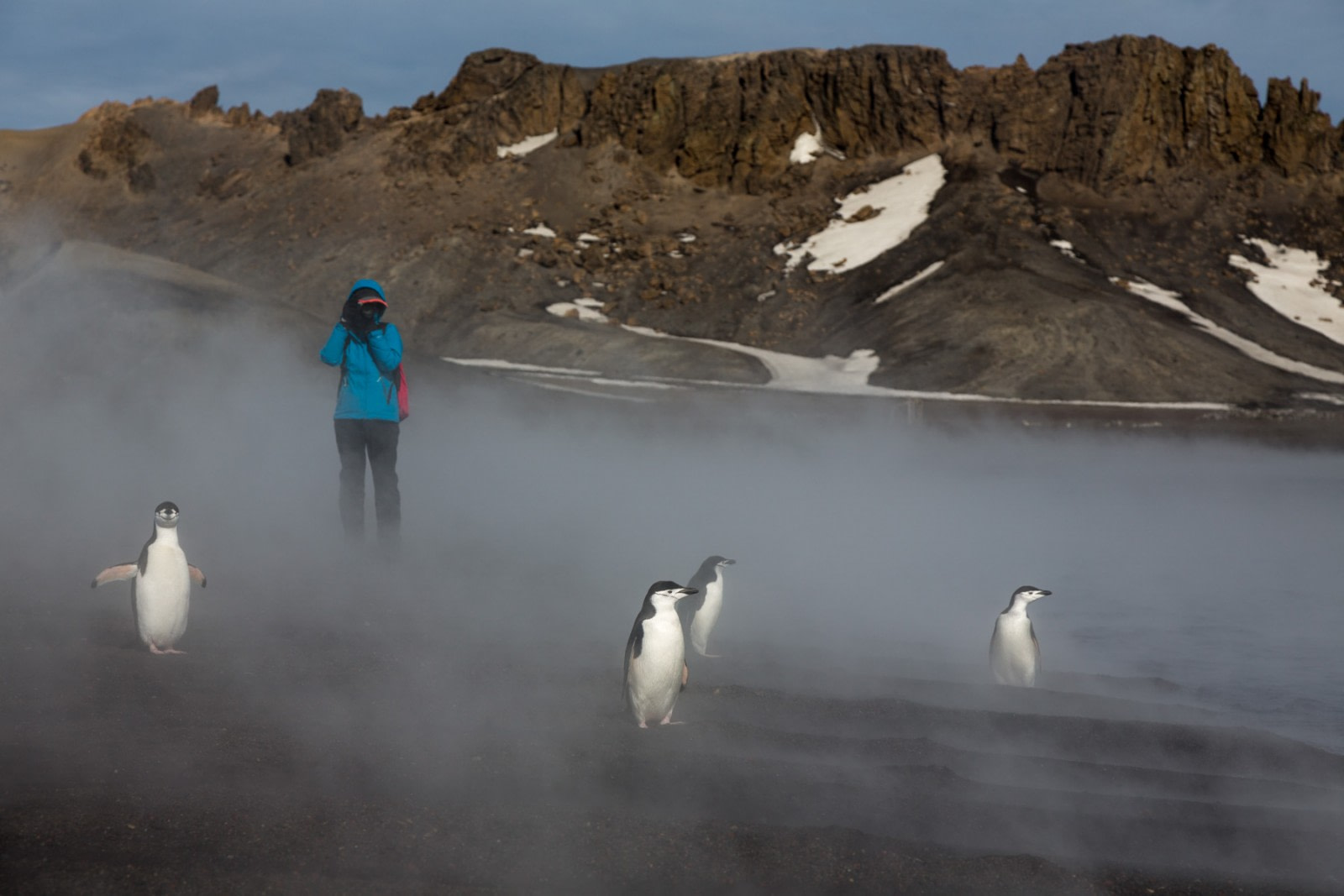

 11 Days / 10 Nights
11 Days / 10 Nights






