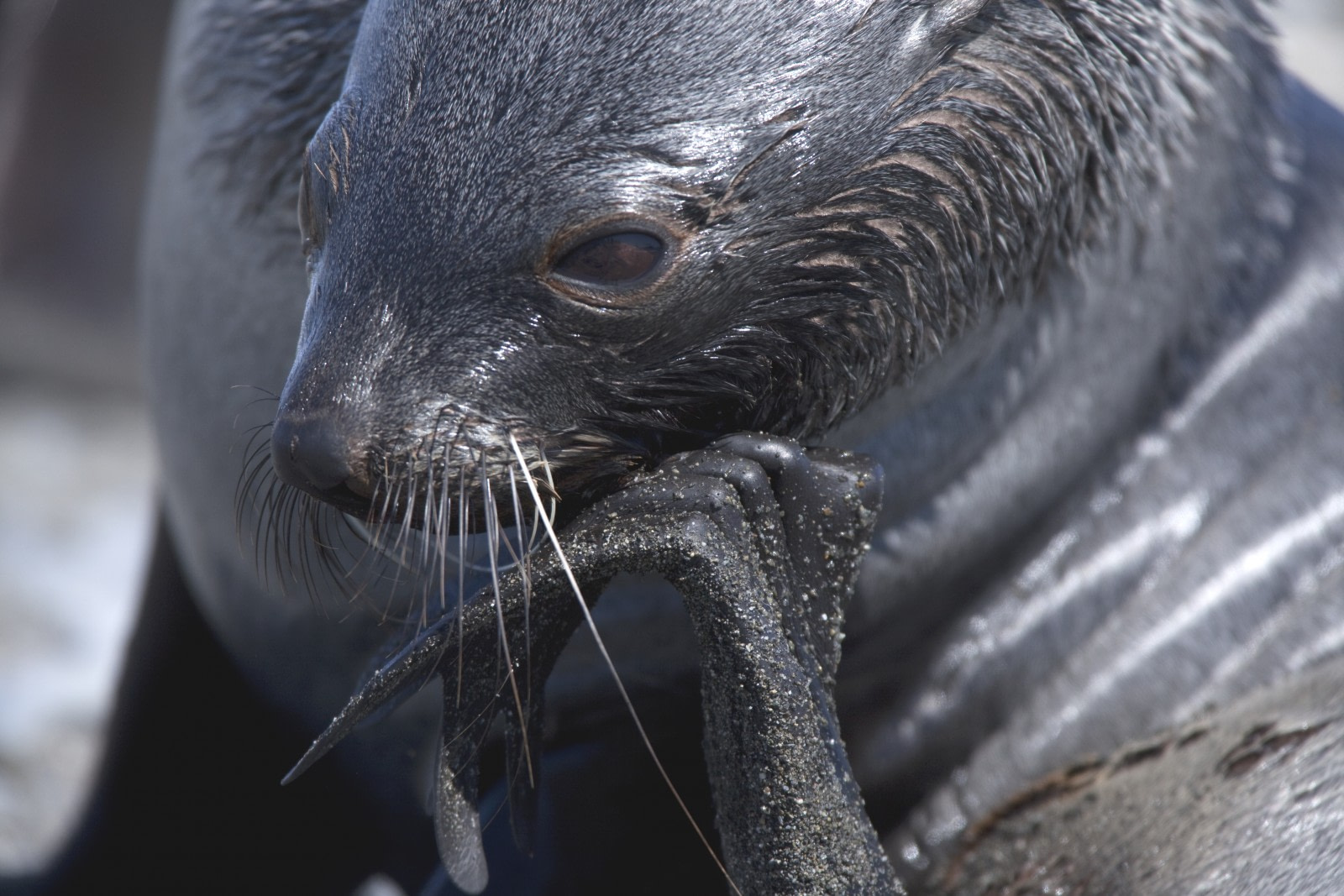
Once hunted to the brink of extinction, the Antarctic fur seal is now one of the most populous and charismatic species of seal you’re likely to encounter during your Antarctica trips. Unlike other members of its large family, the fur seal has external ears, or pinnae, a short snout, and a thick coat of dark brown fur. Male seals tend to be larger than females, with weights ranging from 91 kg (200 lbs.) to 215 kg (474 lbs.).
Diet
The diet of the fur seal primarily consists of various species of Antarctic fish, squid, and a significant amount of krill. This strict diet of sea creatures undoubtedly contributes to their strong odor, which often greets you before you even see them! During foraging trips, fur seals can dive to depths of 180 meters (590 ft.) and hold their breath for up to 10 minutes.
Breeding behavior
From October to November, bulls establish breeding territories along the beaches of Antarctica in hopes of securing a female. Fur seals have historically exhibited polygynous mating behavior, meaning a male will mate with multiple females during one season. During a successful breeding season, a male fur seal, or a “bull,” can mate with as many as 20 females!
Once mates and territories are established, males become increasingly aggressive and defensive. Vocalizations, including a guttural growl, lunging, and displaying, are typical defensive behaviors of male fur seals. Territorial disputes commonly break out between males, leading to serious injuries and even death. After mating, males leave the pregnant females to raise the pups while they seek more females to mate with. Gestation lasts approximately 12 months, and females give birth to one pup. For the next four months, mothers spend their time weaning their pups and feeding out in the ocean.
Predators of fur seals
Even as a top predator in the waters of Antarctica, the fur seal faces significant danger, especially as a pup. Leopard seals, some of the most vicious Antarctic predators, quickly locate pup colonies. The pups are most vulnerable when learning to swim for the first time, especially since they are no longer under their mother’s supervision. Unfortunately, many pups meet their end this way. Killer whales are another predator of the fur seal and will swim into shallow waters, waiting for adults to return from foraging trips.
Sealing in Antarctica
During the 18th and 19th centuries, the United States and Great Britain heavily hunted the Antarctic fur seal throughout its range. Their extremely soft pelts were used to adorn clothing and were highly fashionable and in high demand. Although unregulated hunting had detrimental effects on fur seal populations, this activity was responsible for much of the early exploration of the continent. Unfortunately, this increased hunting pressure brought the fur seal to the brink of extinction by the early 20th century. The outlook was grim for the seals, but even with a greatly reduced population, conservation and preservation were still possible.
In 1972, the Antarctic Treaty System established the continent and waters of Antarctica as protected areas where no hunting or collecting of seals or other marine mammals could occur. With this intense hunting pressure relieved, fur seals were able to proliferate throughout their range and surpass their pre-sealing population numbers.
Conservation
Currently, the Antarctic fur seal is a protected species under CITES (Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species) and a branch of the Antarctic Treaty System dedicated to seals called the Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Seals. According to these stringent laws, no fur seals can be “taken,” or collected and transported internationally in any way for any purpose without government-issued permits. Violations of these laws can result in fines and even jail time for repeat offenders.
Since the establishment of these laws, fur seal populations have increased exponentially throughout Antarctica. Researchers suggest that there may be between two and four million individuals breeding at South Georgia, where whaling pressure was exceptionally high during the 19th and 20th centuries. In the absence of whales, krill populations soared, providing a steady and reliable food source for other Antarctic wildlife species, including the fur seal. This uninterrupted food source allowed populations to sharply increase.
Many researchers have become increasingly concerned with the fur seals’ population explosion and overcrowding of individuals at breeding and haul-out sites, which has directly linked to a decrease in Antarctic grass populations. There simply isn’t enough room to accommodate millions of seals! As the population continues to increase, researchers are beginning to suggest the loosening of conservation laws to prevent damage to sensitive plant species. Further action on this issue has yet to be taken.
Like many other sea-dwelling species, the Antarctic fur seal faces an uncertain future with the increase of ocean pollution, plastic abundance, and global climate change. Changing ocean temperatures directly influence prey abundance and availability, which can have potentially negative effects on their population size.
Where to see fur seals
One of the best places for Antarctic fur seal spotting is South Georgia. You’ll most likely smell them before you see them, but make sure to keep a careful eye out! Their summer fur blends in perfectly with the lichen-covered ground, camouflaging them with their surroundings. Their aggressive behavior is well documented, and they have even been known to chase and bite humans that tread a little too close. Make sure to keep a safe distance!
Related Trips
Blog



The bowhead whale, whaling about the Arctic

Penguins, Albatrosses, Petrels: The Winged Wildlife of South Georgia

Highlights from the First Arctic Voyage of Hondius

15 Fantastic Photos of Antarctica

Weddell Sea: the Original Antarctic Adventure

Eight Ultimate Antarctica Adventures

Visiting the Nearly Unknown: New Zealand’s Campbell Island

Fierce and Feathered: the Skuas of Antarctica

Freshwater ecosystems in the Arctic

Traditional Lifestyles of the Inuit

The Giant Petrels of King George Island

Path of Polar Heroes: Hiking Shackleton’s Historic Route

Orcas of the Polar Seas
First to the North Pole: Five Failed but Brave Expeditions

Navigating by touch through the sea ice

The First Overwintering Hut in Antarctica

Polar Amore: 14 Wildlife Pics to Warm up Your Valentine’s Day

Living the Antarctic Dream

A Day of Whale Watching in Antarctica







 28 Days / 27 Nights
28 Days / 27 Nights
