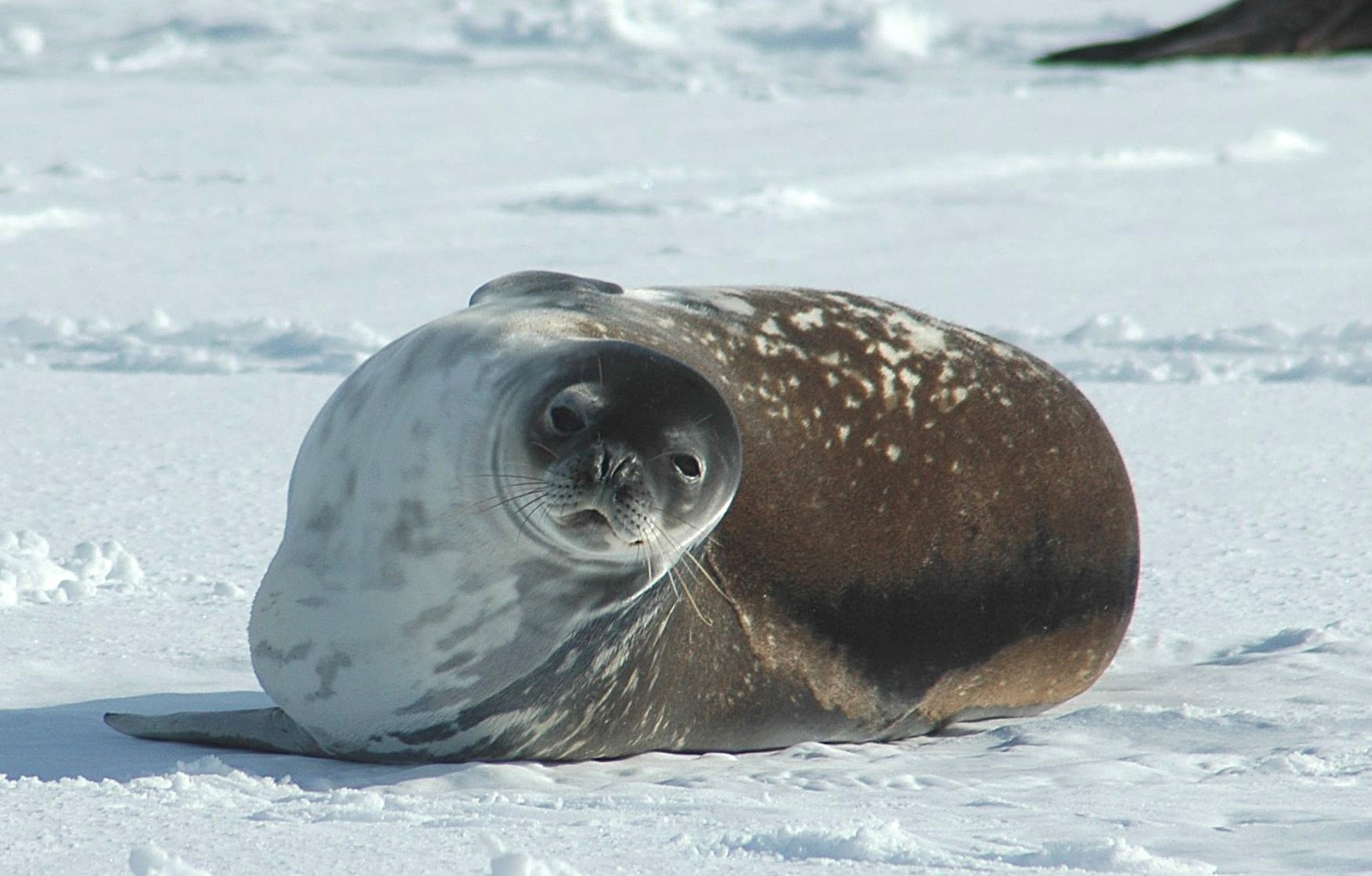
Weddell seals inhabit some of the coldest and darkest waters deep within the Ross Sea ice, making them the southernmost naturally occurring mammals on Earth. During the winter and summer months, their movements are largely governed by the presence of sea ice and the availability of suitable breathing and exit holes.
While the seals look ‘cuddly and cute’ with their slightly upturned mouths, dark brown eyes, and whiskers, at around 3 meters in length and weighing 400-500 kilograms, Weddell seals are one of the top predators you can find on an Antarctica cruise that feed on fish species. Antarctic toothfish are speculated to be the important dish for Weddell seals, though the Weddell Seal is selective in what part of the toothfish it eats, with only the flesh of large toothfish taken fed on.
Studying the lifecycle of Weddell seals
Weddell seals in spring, after foraging in the outer pack ice, return to inshore fast ice locations to breed and give birth. Male seals occupy underwater territories beneath cracks in the sea ice, allowing easy access to the surface. In McMurdo Sound, adult Weddell seals begin to congregate in pupping colonies in early October, with the location of pupping colonies dependent on tidal action, wind, and glacial movements.
In each colony, there can be as many as 250 Weddell seals found. Pups are born on the sea ice in late October and November. Females remain on the ice with their young to nurse and commonly have just one pup per year. A typical pup weighs around 29 kilograms, reaching around 110 kilograms within six weeks. A pup is introduced to the water very early on: 7-10 days after birth.
Weddell seals leave Erebus Bay and disperse throughout the Ross Sea in late summer, with adult Weddell seals returning annually to the same pupping colony. However, juvenile members disperse from the pupping colonies where they were born and occupy pack-ice regions until they reach maturity at around 3-6 years old.
In the past, Weddell Seal numbers were under pressure from harvesting by research stations located in McMurdo Sound, specifically, the United States’ McMurdo Station and New Zealand’s Scott Base. While Weddell seals were not commercially hunted, they provided food for each base’s resident dog teams. In many marine mammals, there only needs to be a slight change in adult survival to influence population growth, and so it is likely the hunting of Weddell seals impacted population numbers in the Ross Sea.
Since 1968, scientists have been recording Weddell seals in McMurdo Sound, representing one of the longest continuous field investigations of a long-lived mammal in the world. Over the past nearly 50 years, researchers have tagged more than 23,000 Weddell seals and over 240,000 re-sightings have been logged in the database. The tagging information includes year tagged, age at tagging, sex, location, and year last sighted. There has been a specific emphasis placed on maintaining and enhancing annual demographic data, resulting in all pups born within the study area being tagged since 1973. This long-term project provides invaluable data on population and ecosystem processes, enabling scientists to understand the linkages between environmental conditions and demographic processes in Antarctica.
In one study, researchers from the University of California, Santa Cruz, and the University of Alaska investigated Weddell Seal behavior over the dark winter period when heavy sea ice prevails. The study involved fitting 22 Weddell seals with Conductivity Temperature Depth-Satellite Relayed Data Logger tags that recorded their dive depths and locations. The study recorded 52,000 dives, with the research finding the seals dived on average between 15-270 meters, with max dives ranging from 40 to 1188 meters. When looking at the spots the seals dived, the study found several ‘hot spots’ where numerous dives were made. In a fascinating discovery, the data also indicated several Weddell seals traveled over 1,000 km from the area the tags were fitted.
In a recent study funded by the National Science Foundation, New Zealand Antarctic Research Program, University of Canterbury, and the U.S. Antarctic Research Program, Dr. David Ainley, along with other researchers, compared ground counts of Weddell seals over the period 1959-1968 with counts using high-resolution satellite imagery during 2008-2012. The study – published in the Marine Mammal Science – found many fewer Weddell seals at two major molting areas in the western Ross Sea. However, the study did find the breeding population in McMurdo Sound to have appeared to recover following their harvest in the 1960s. The scientists speculate the population decline could be the result of altered food webs in the region, possibly due to industrial fishing targeting a seal prey species.
Nonetheless, populations of Weddell Seals will likely come under pressure with calving of ice becoming more frequent in Antarctica with rising temperatures. In 2000, iceberg B-15 calved off the eastern portion of the Ross Sea Ice Shelf in McMurdo Sound. Until 2006, fast ice increased in thickness, extent, and seasonal persistence, with extensive fast ice along the Victoria Land coast, Ross Sea exceeding typical coverage by a factor of five. This impacted Weddell seals as sea ice conditions determine the abundance of food resources and access to breeding sites in Erebus Bay. In a study conducted by Lacey Briars, the researcher found a noticeable decrease in Weddell Seal pup numbers between 2000 and 2006, with a significant rise in pup numbers in 2007.
Recruiting Weddell seals as scientists
To understand not only Weddell seals but also how, when, and where the global currents that link all the world’s oceans are formed in Antarctica, Dr. Regina Eisert of Gateway Antarctica, University of Canterbury, with support from Antarctica New Zealand, led an international team of researchers that attached satellite-linked Conductivity, Temperature, and Depth recorders to 10 Weddell seals at the New Zealand station Scott Base. Using the Weddell seals as data collectors, scientists not only recorded the seals’ dive depths but also water temperature, ocean salinity, and depth: the specific data required to describe the ocean structure and function. What makes the use of Weddell seals as reliable scientists is the seals are able to collect this information over the autumn-winter period to spring period, but most importantly over the harsh winter when the area is inaccessible to conventional sampling using ship or ocean buoys. When they resurface, the recorders can transmit the information collected to circulating satellites, and as Weddell seals inhabit the fast-ice, they can collect high-quality oceanographic information on the structure of the water column. Another aspect of Weddell Seal behavior that makes them ideal data collectors is while some Weddell seals roam across wide areas of the Ross Sea, providing a wide spatial structure of the water, the majority of the seals stay in the same area for days or weeks feeding in the same spot. As these seals dive and resurface, they provide multiple casts of the water structure in that area, providing scientists data on ice formation over winter and ice-melt in spring. The project is part of the larger Australian government-funded Integrated Marine Observing System (IMOS) that has been collecting data with seals since 2008. The program collaborates with the French, United States, British, and Norwegian and now New Zealand Antarctic programs, with the seals collecting over 70% of oceanographic profiles south of 60°S.
Blog



Peaks, Fjords, and Auroras: 14 East Greenland Attractions

Svalbard’s 12 Most Iconic Animals

All About Ice: Glaciers and Icebergs of the Arctic and Antarctica

12 Tips to Help Keep Birds Safe During an Antarctic Cruise

Three Antarctica Cruise Deals

The Arctic Borderland of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard
First to the North Pole: Five Failed but Brave Expeditions

The History of Antarctica in Maps

Visiting the Nearly Unknown: New Zealand’s Campbell Island

Flowers in Antarctica

The Secret Life of Glaciers: How They Form, Move, and Melt

Weddell Sea: the Original Antarctic Adventure

Taking the Polar Plunge

15 Fantastic Photos of Antarctica

Six Facts About the Crabeater Seals of Antarctica

Antarctic Explorer’s Voyage

Antarctica’s first Marine Protected Area

The Wildlife of Antarctica’s Seas and Skies

The disastrous expedition in the Arctic west






