Long before human eyes ever beheld Antarctica, the ancients were convinced that it existed – or at least something like it.
Ptolemy, a Greco-Roman astronomer who lived from roughly 100 to 170 CE, thought that an enormous far-southern landmass had to exist to provide a planetary counterweight to the large continents of the north. This hypothetical region, which had never been seen much less mapped, even had names: The term “Antarctic,” coined by Greek geographer Marinus of Tyre back in the 2nd century, referred to an imagined area opposite the Arctic Circle; and in the 5th century, the Roman scholar Macrobius included a southern territory called Australis (Latin for “of the south”) on his maps.
Later medieval references to Terra Australis Incognita, or “Unknown Land of the South,” would elaborate on these old-fangled theories, and maps drawn between the 15th and 18th centuries often included it at the bottom. None of these names or renderings truly referred to the Antarctica we know today, since it would be hundreds of years before the continent was actually seen, but they did fuel a geographical myth that persisted for centuries.
A number of later voyages through the late 1700s charted many of the waters into which Terra Australis was thought to extend, and either reduced or eliminated it from maps altogether. It was not until 1820 that a confirmed sighting of Antarctica did occur. Even so, the centuries-long cartographical transformation of Terra Australis into Antarctica is a fascinating record of the evolution of modern geography.
Below is a list of maps that, while by no means complete, follows this evolution in some of its key phases. More than mere directional aids, these maps are beautiful fusions of art and science crafted centuries before the benefit of modern navigational equipment.

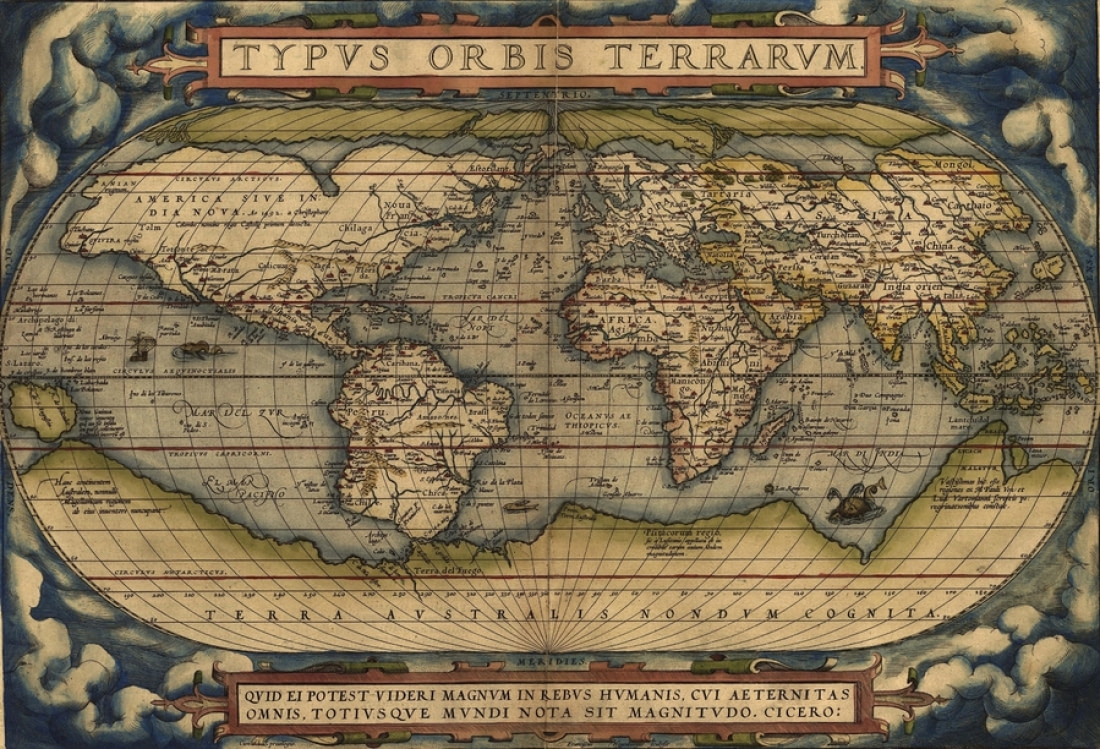
1570: Abraham Ortelius and the Theater of the World
One of the most famous maps on which Terra Australis first appears forms a central segment of the world’s first modern atlas. Flemish cartographer Abraham Ortelius’s renowned Theatrum Orbis Terrarum, or “Theater of the World,” is a compendium of all the latest maps drawn by his contemporaries, representing the sum of 16th century cartographical knowledge.
Ortelius is among the most famed mapmakers of the Dutch golden age of cartography, which occurred between the 16th and 17th centuries. Among the chief sections of his atlas is the Typus Orbis Terrarum, a world map that depicts Terra Australis as being by far the largest landmass in the known world: It fills most of the space south of the Tropic of Capricorn, nearly touching the southern tip of South America, and extends all the way to New Guinea. Ortelius’s atlas, a pivotal development of world geography, was a mainstay of navigation and was regularly updated over the ensuing decades.
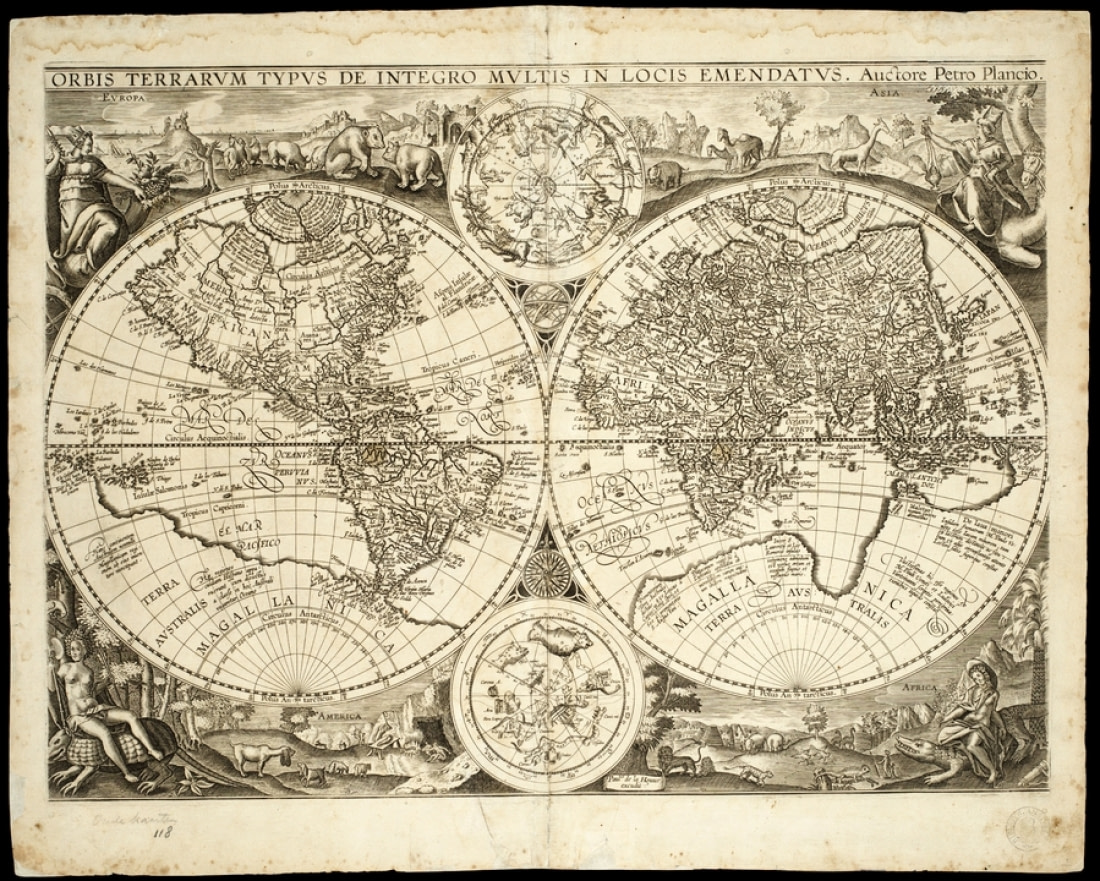
1590: Petrus Plancius and the Orbis Terrarum
Known more for its coverage of the Arctic and Far East than for its depiction of the far southern landmasses, Dutch-Flemish cartographer Petrus Plancius’s Orbis Terrarum represents Terra Australis in much the same way Ortelius’s Theatrum did twenty years earlier.
Originally completed in 1590, Plancius’s world map depicts Antarctica as nearly reaching the southern end of South America, like Theatrum. It also shows the continent extending north almost to New Guinea and Java, like Ortelius’s map, reaching far into the Indian Ocean and terminating relatively close to the southern shores of Africa.
Plancius was not known only for cartography, however. He wrote navigational guides, innovated a new system for determining longitude, and collaborated with Dutch mapmaker Jacob Floris van Langren on a celestial globe that depicted several southern constellations not previously illustrated in maps.
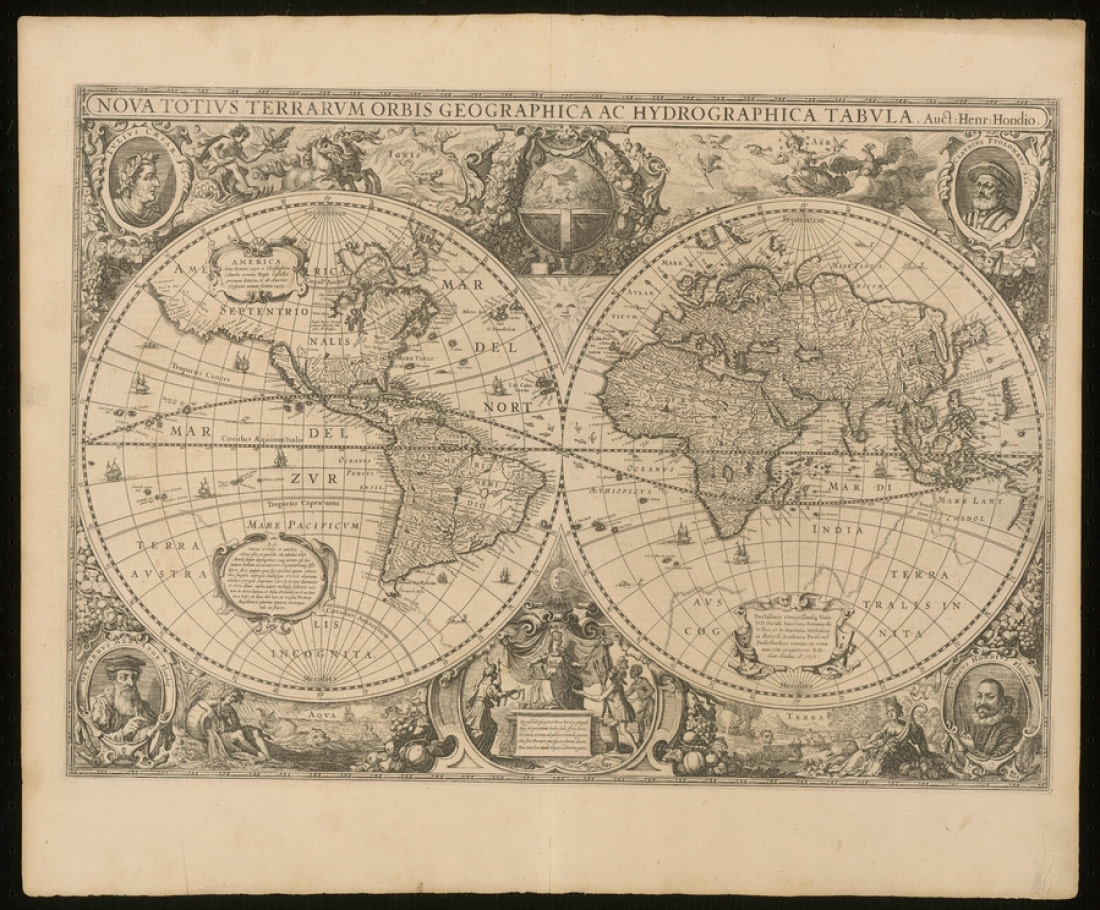
1630: Henricus Hondius II and the Nova Totius
Forty years after Plancius made his mark on the cartographical world, Henricus Hondius II finished his own world map, the Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Geographica ac Hydrographica Tabula. As if that weren’t enough of a mind-boggling mouthful, there happened to be two Henricus Hondiuses practicing cartography in the Dutch Republic at the same time. Though they were contemporaries, they were not related, and in fact Hondius I was Flemish born despite later settling in Amsterdam – where, incidentally, Hondius II was born.
Like Plancius, Hondius II worked with materials originally produced by an earlier cartographer, Gerardus Mercator. Mercator, one of the few major cartographers who for reasons of concision is not represented in this list, created his own world map in 1569 that shows Terra Australis in much the same way Ortelius would in his 1570 atlas and Plancius would in his 1590 world map.
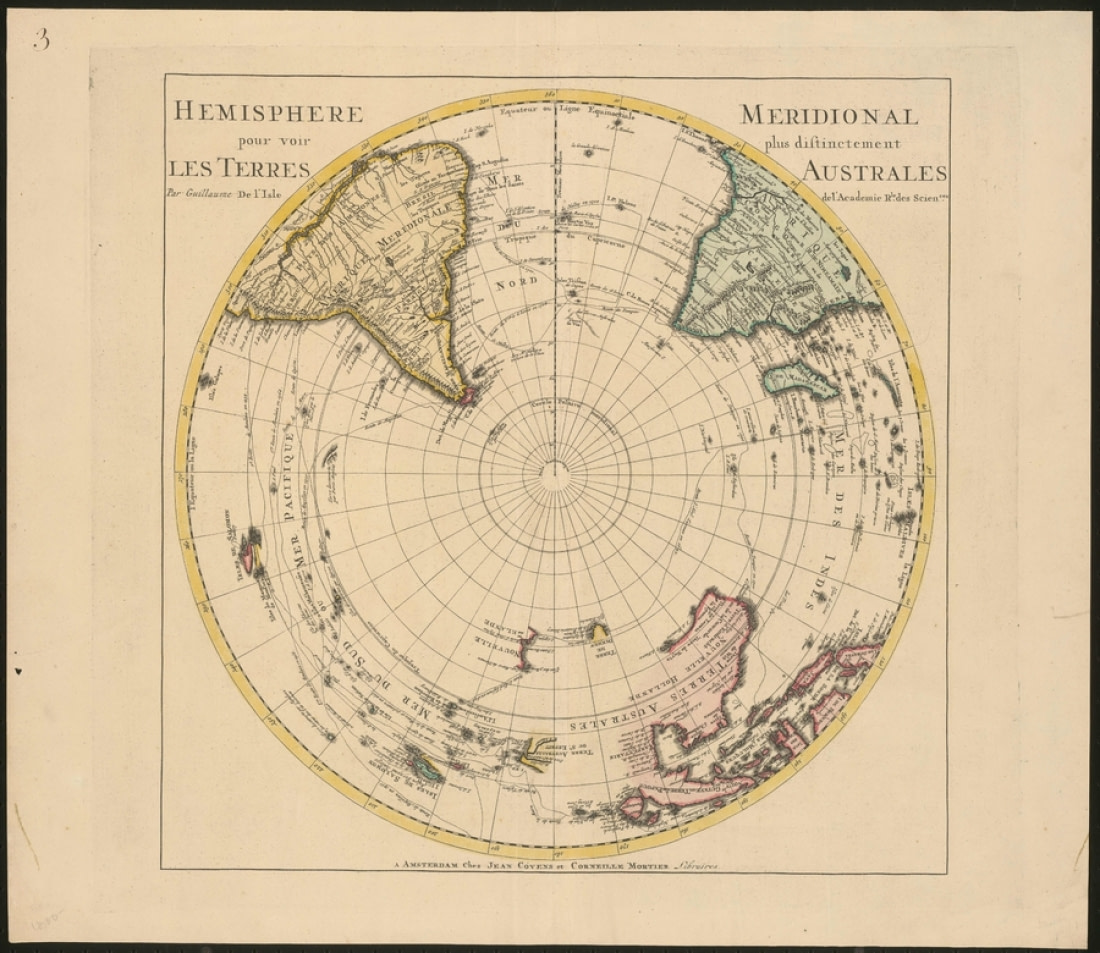
1741: Covens & Mortier and the vanishing Australis
By the 18th century, the Dutch cartographical golden age had produced a number of enormous (and enormously successful) map publishers. One of the largest was Covens & Mortier, founded in Amsterdam by Johannes Covens and Cornelius Mortier.
Among their long tradition of impeccably drawn maps was a rendering of the Southern Hemisphere that does not depict Terra Australis at all. This was a common result of further exploration into the southern seas: As navigators began to learn how far the seas extended to the south, the available room for the once-colossal Terra Australis naturally diminished.
In fact, explorations undertaken in the previous century had already disproved much of the hypothetical southern continent’s dimensions. Tierra del Fuego, for example, was revealed as being smaller than originally thought, and Australia was found to not be part of a larger continent. In 1770, James Cook continued this reduction by showing that New Zealand was not part of Terra Australis, which he deduced must be located within the polar region of the Southern Hemisphere.
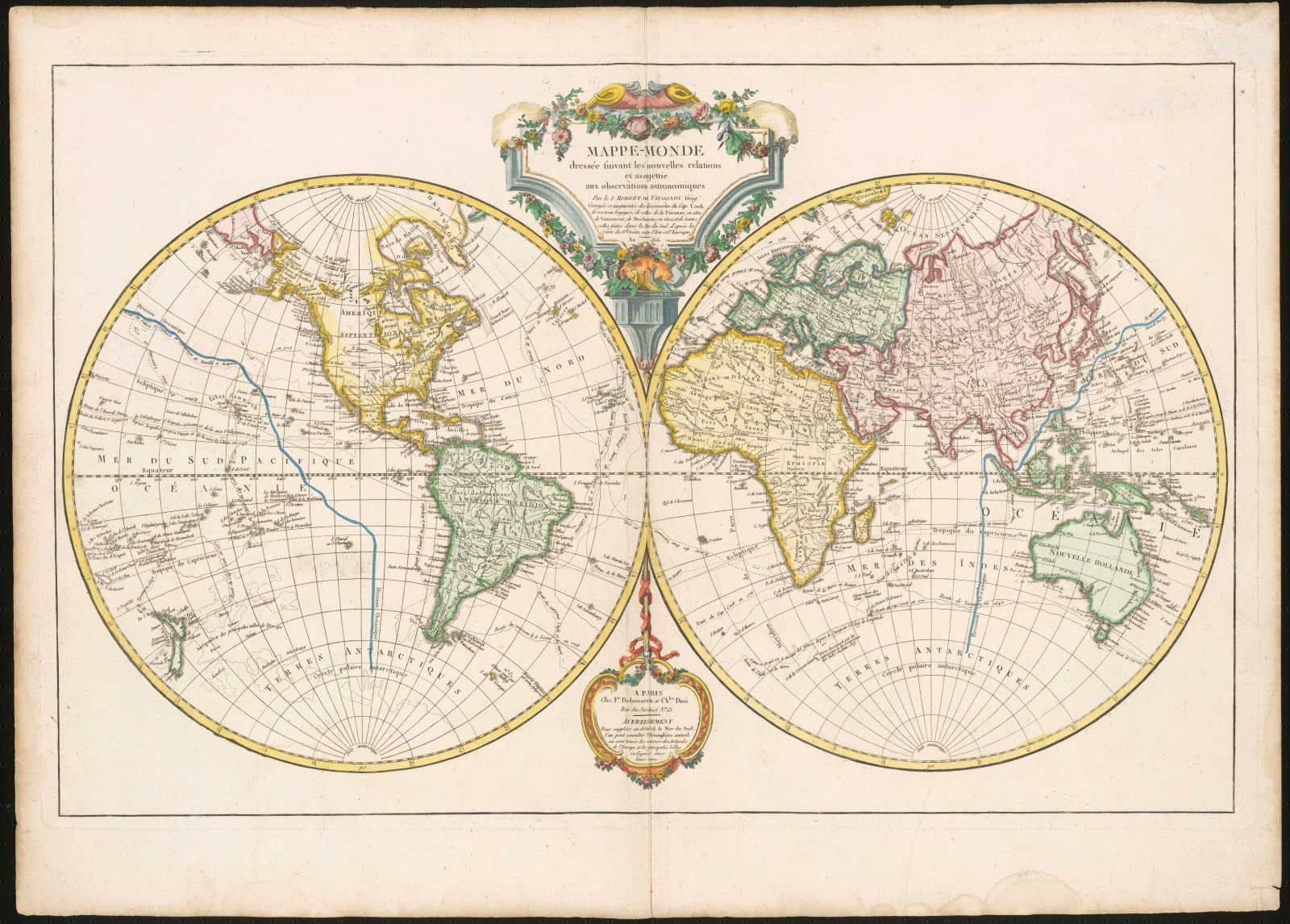
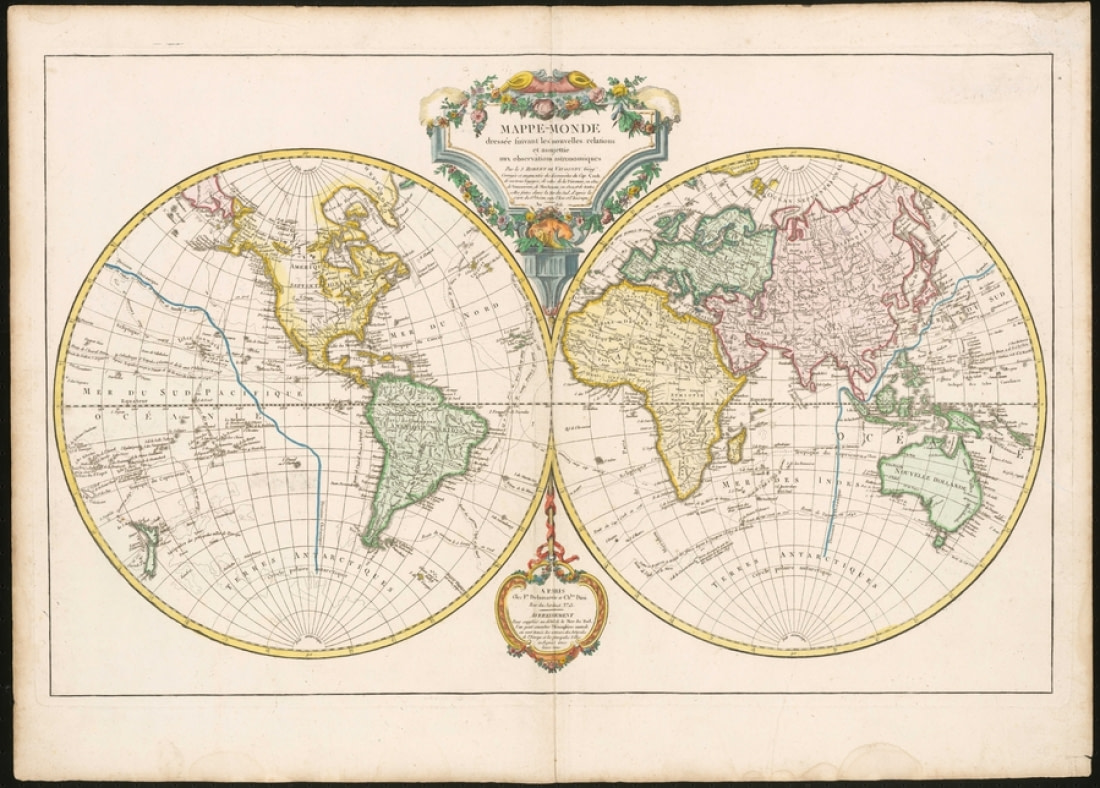
1749: Du Vaugondy and the Mappe-Monde
Gilles and his son, Didier, two of the 18th century’s most well-known French cartographers, produced some of the last maps to predate the confirmed 1820 sighting of Antarctica. One of their most extensive maps, the 1749 Mappe-Monde, also omits Terra Australis. The landmass is replaced with the unknown area of Terres Antarctiques, translating simply to “Antarctic Lands.” The version of the Vaugondy map shown in this image was released in 1816 and includes updates resulting from the discoveries of multiple explorers after the original 1749 release.
Other parts of the world are nearly as blank as the Antarctic region, such as America’s Pacific Northwest. It would be some time before this area would be filled in, much like Antarctica, but if nothing else these blank portions suggest that cartography was moving away from its reliance upon ancient conjecture. The system and science of map making, advancing all the more rapidly with the innovations spurred by the Age of Discovery, would in turn progress map by map toward the state we find it in today.
Blog



Kayaking In Greenland

Everything you need to know about Antarctic icebergs

Deep Sea Dwellers: 10 Facts about The Antarctic Giant Isopod

10 Bountiful Blue Whale Facts

Antarctic Explorer’s Voyage

Large and in Charge: Antarctica’s Southern Elephant Seals

Where the Polar Bears Roam

A Day of Whale Watching in Antarctica

Penguin Wisdom: Life Lessons from Our Favorite Flightless Birds

Graham Land: A landscape dominated by volcanoes

Guidelines for visitors to Antarctica

The Arctic Borderland of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard

Diving in Antarctica: The Ultimate Underwater Experience

How Arctic Wildlife Differs from Antarctic

Keep It Green: Our Commitment to Sustainable Polar Travel

Polar Diving: A Supreme Underwater Adventure

8 Whales You Might See During Your Antarctica Cruise

Five Reasons to Love St. Helena

Seizing the Season: Spitsbergen’s Late Spring, Early Summer