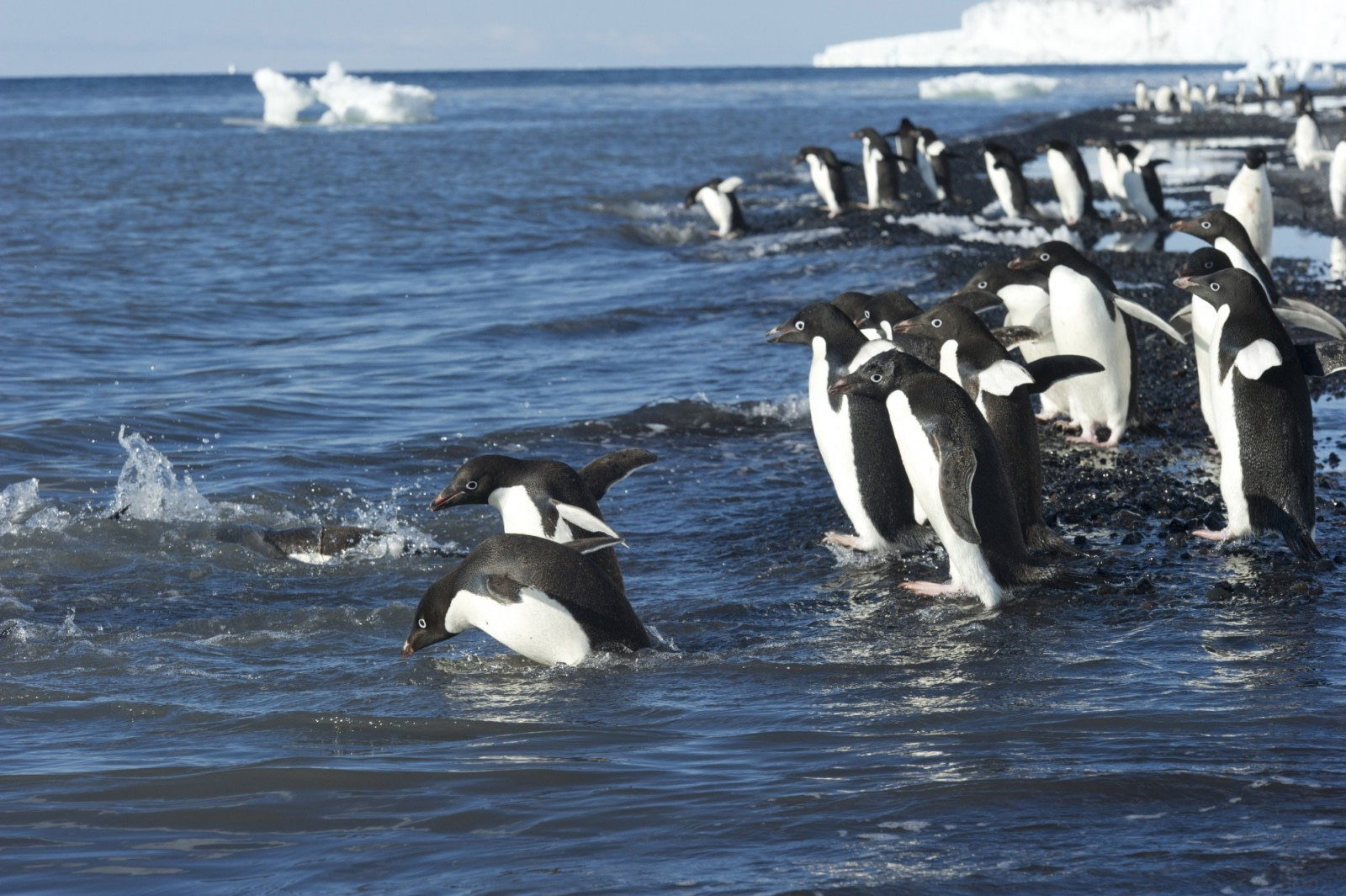
The Adélie penguin population in the Ross Sea has reached its highest numbers in 30 years, with up to a million breeding pairs during the summer. This accounts for about 38 percent of the entire Antarctic Adélie population.
Research by scientists Dr. Phil Lyver and Dr. Mandy Barron, along with Antarctic New Zealand and Bartonk Solutions, has shown that Adélie penguin colonies on Ross Island in the Ross Sea have been growing at an average rate of 6 percent annually since 2001. This is a significant recovery from the 1980s and 1990s when the population was declining by about 2 percent per year.
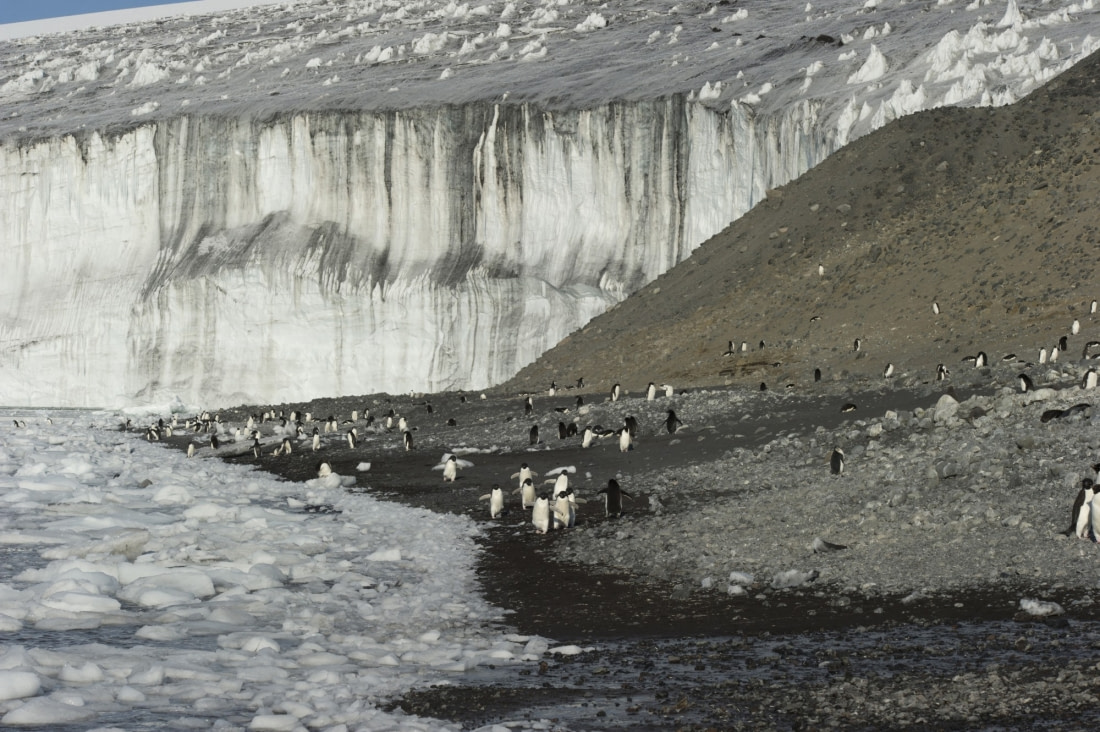

The importance of monitoring Adélie populations
Adélie penguins serve as an indicator species for scientists studying changes in the marine ecosystem due to commercial fishing or climate change. They are particularly useful for monitoring because:
- They consume krill, a crucial part of the food web. Changes in krill availability can affect not only Adélie penguins but also other predators like seals and whales, leading to fluctuations in their populations.
- They rely on sea ice, which is expected to be impacted by climate change in terms of extent and thickness.
Additionally, Adélie penguins are easier to monitor compared to other Antarctic predators. They breed during the summer, making them accessible during 24-hour daylight, and they return to the same breeding sites on land each year, unlike whales and most seals that breed at sea or on pack ice.
How to count Adélie penguins
Scientists monitor Adélie populations by studying the reproductive and foraging activities of penguins at three colonies on Ross Island:
- Cape Royds with an estimated 3,500 breeding pairs
- Cape Bird with an estimated 60,000 breeding pairs
- Cape Crozier with around 150,000 breeding pairs
Aerial counts of Adélie penguins
Since 1981, scientists have been counting Adélie penguins through aerial reconnaissance photography from helicopters or C130 Hercules aircraft. This is done in late November or early December to coincide with the incubation phase of breeding, allowing for accurate counts of breeding pairs and establishing baseline data on population trends.
Adélie penguins nest in large colonies, leading to competition for breeding space, food, and partners. These social factors, combined with physical factors like food availability, determine breeding success.
To measure social impacts, scientists fit individual penguins with metal bands on their left flippers. Each band has a unique number that can be read from a distance, allowing scientists to track individual penguins and study their survival, lifespan, breeding habits, and migration patterns.
Breeding success is also measured by sampling the condition of chicks. Chicks are weighed and measured to calculate a condition index, which helps compare chick health across different colonies and years.
Measuring Adélie foraging efforts
The study also examines parental foraging efforts by fencing off a group of 50 breeding pairs. The only way in or out of this area is over an electronic weighbridge. Each penguin has a small tag injected under the skin around the neck, acting like a barcode.
As penguins cross the weighbridge, sensors read the tag, weigh the bird, and record the direction of travel. This data helps scientists understand how long the birds spend at sea, how much food they bring back, and any differences in foraging behavior between males and females.
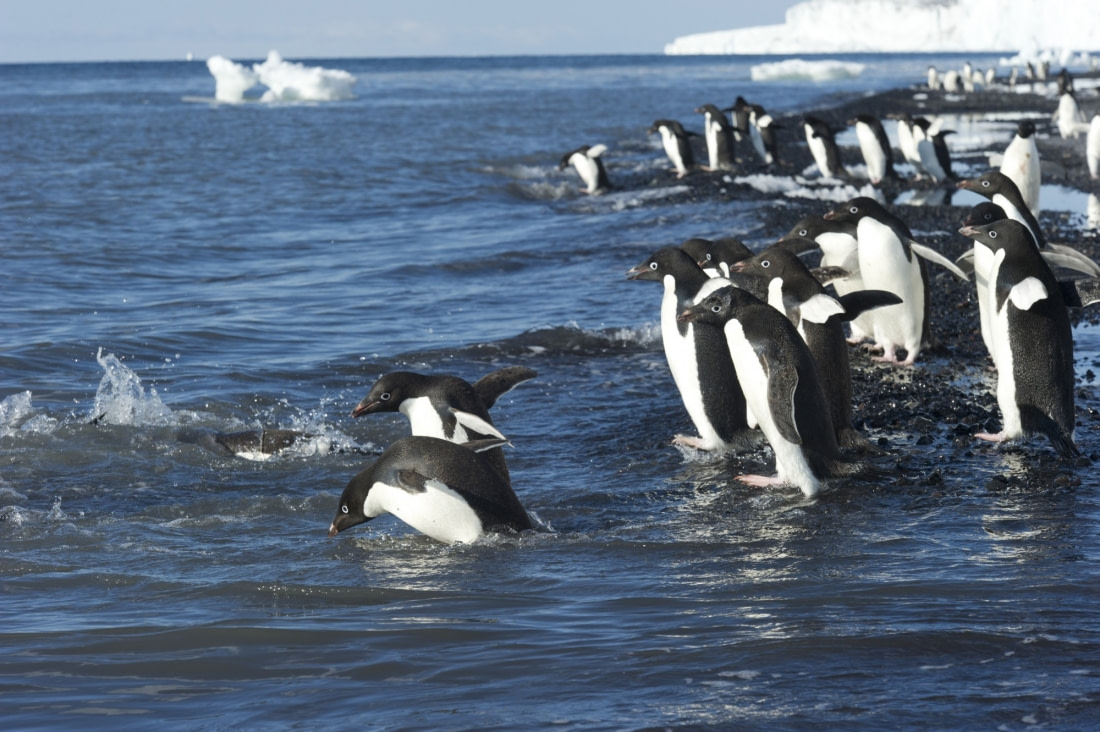

In addition to tags, scientists use time depth recorders, satellite tags, and transmitters to study penguin behavior at sea. These devices are temporarily attached to the penguins' feathers and emit electronic pulses, allowing researchers to track their movements and activities.
Signals from these devices help determine specific behaviors, such as diving, resting on ice, or swimming. Location data is obtained through triangulation, providing insights into the size of foraging areas, overlap with adjacent colonies, and distance to feeding grounds.
Scientists are investigating what drives annual variations and increases in colony size. Adélie penguins thrive in areas with around 15 percent sea-ice coverage, which provides resting spots without limiting access to open water for foraging.
With rising sea temperatures, there is concern that around 75 percent of Adélie penguin colonies (70 percent of the breeding population) in Antarctica may decline or disappear by 2050. However, Ross Island colonies are located south of 70°S, potentially offering some protection from these changes.
Blog


First to the North Pole: Five Failed but Brave Expeditions

The Small but Social Commerson’s Dolphin

Antarctica’s Hourglass Dolphin

The First Buildings in Antarctica: Borchgrevink’s Historic Huts

Not Eskimos: 10 Enlightening Facts About the Inuit

Cruising Solo: The Benefits of Single-Passenger Polar Travel

Why a Polar Diving Cruise Should be Your Next Great Decision

Encounter with the emperor penguin in Antarctica

Graham Land: A landscape dominated by volcanoes

10 Weather-Fueled Facts about Antarctica

Islands of the Blessed: Things to Do Around Cape Verde

Arctic on Foot: Hiking and Snowshoeing the Far North

Six Seal Species You Might See On Your Greenland Cruise

The World Is Changing for Greenland's Native Inuit People

Arctic Seals

Everything you need to know about Antarctic icebergs

Eight Antarctic Misconceptions

Polar Cruises: The Ultimate Icebreaker

The Norse Settlement of Greenland






