A Greenland cruise offers a journey into a rich history filled with intriguing details that captivate polar expedition enthusiasts. Among the most fascinating historical aspects is the fact that Vikings once ruled this land. Anthropologists and climate scientists have long studied Greenland to pinpoint when and why the Vikings left. Recent findings have shed new light on this historical culture.
What Made the Vikings Leave?
In 2011, researchers suggested that an extreme cold snap, known as the Little Ice Age, was likely responsible for the Viking exodus from Greenland. By running climate models from that era, scientists determined that Greenland began a cooling period around 1100 CE. This conclusion was drawn from data collected from lakes in western Greenland near a known Norse settlement.
Ice cores revealed that the area’s average temperature dropped by 3.9°C (7 degrees Fahrenheit) between 1100 and 1180 CE. Although this may not seem significant, such a rapid change likely increased sea-ice levels and shortened the crop growing season. Consequently, access to food and previously used trading and sailing routes would have diminished, forcing the Vikings to seek better living conditions.
It is known that Greenland’s Vikings endured these harsh conditions for at least 10 years during the mid-1300s, losing much of their cattle due to cold summers and brutal winters. However, recent findings suggest they may have stayed in the region for a much longer period.
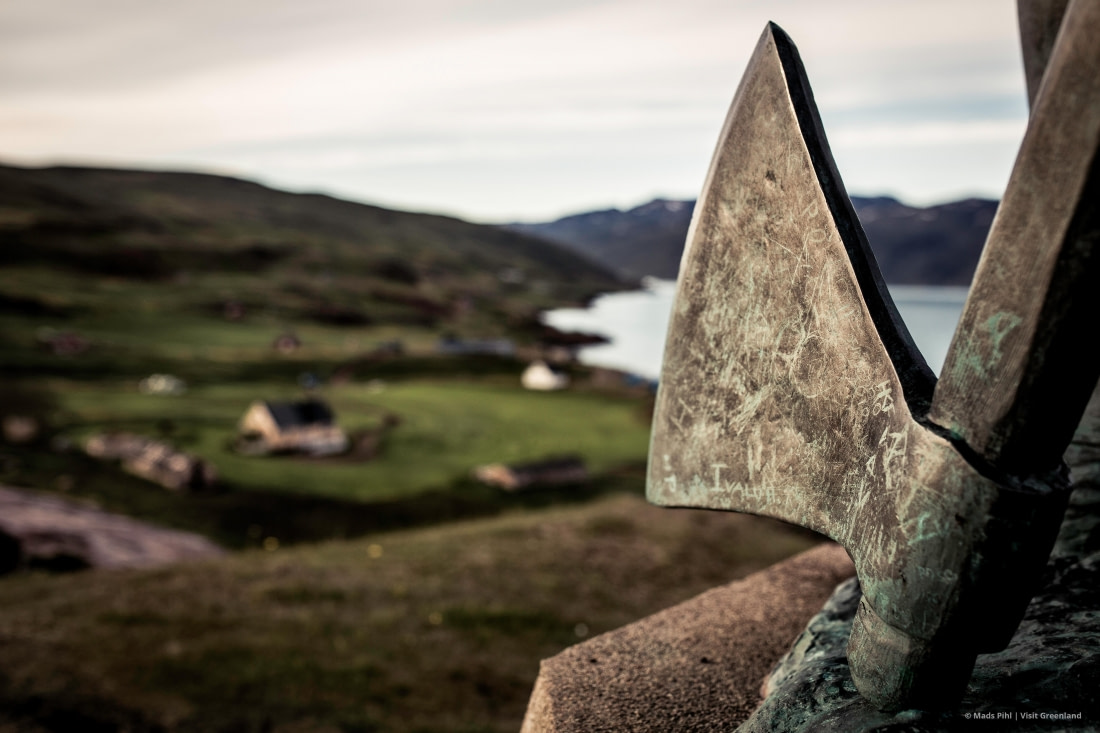

New Research Fills in the Past
From 2011 until early 2015, the Little Ice Age theory was widely accepted as a plausible explanation for the Vikings' departure. However, this idea has come under scrutiny. While it is undisputed that the Little Ice Age occurred and impacted Viking life, new information suggests the Vikings endured Greenland's harsh climate for much longer than previously thought.
Archeologist Christian Koch Madsen has conducted extensive landscape studies to determine how the Vikings were affected by the colder climate. Madsen’s findings suggest that the Vikings lived in Greenland for an extended period during the Little Ice Age and that previous population estimates were significantly off.
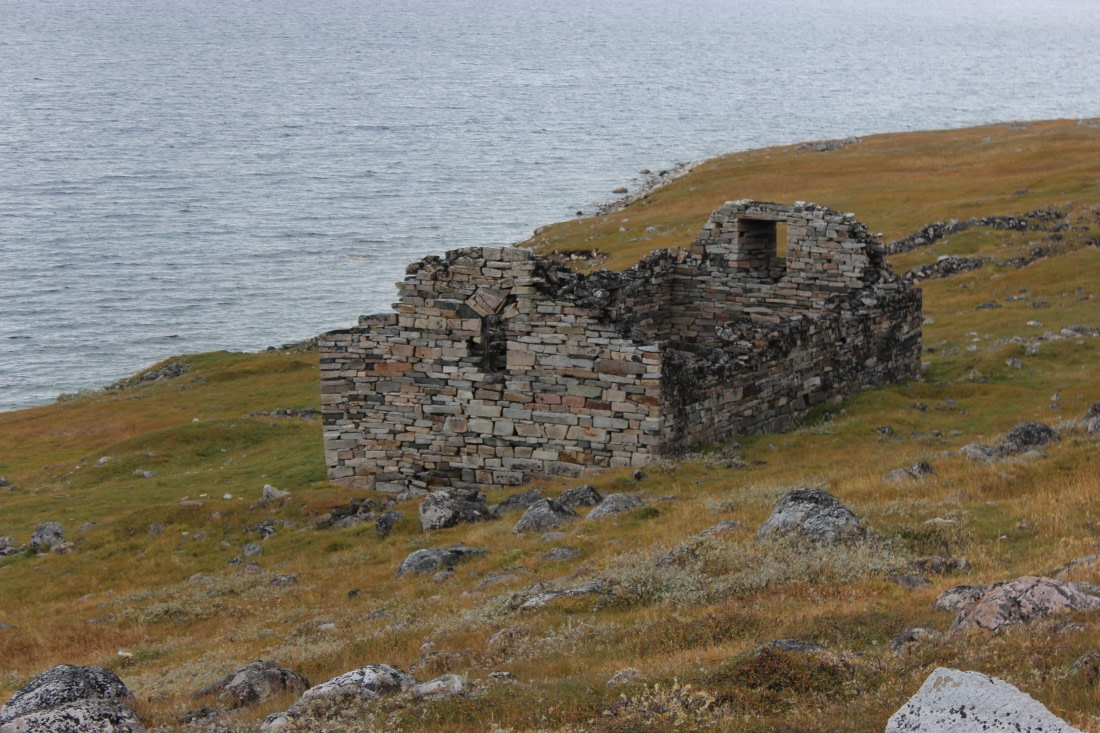

The Population Disparity
The 2011 study assumed that around 6,000 Vikings lived in Greenland when the Little Ice Age began. This led researchers to believe that a massive evacuation occurred early during this cold period, as they found evidence that the population decreased by several thousand. However, Madsen’s landscape studies suggest that no more than 2,500 people lived in Greenland as the Little Ice Age began to lower temperatures.
This disparity could explain why earlier researchers thought most Vikings left their Greenland settlements within 10 years in the mid-1300s. A population drop from 6,000 to 2,500 would indicate a mass exodus. Conversely, if the population was closer to 2,500 initially, it would suggest that the Vikings continued to live and adapt in Greenland’s coldest regions. Madsen believes the Vikings persisted for at least 200 years as the climate grew colder, adapting by shifting from farming to trapping.
While we cannot be certain which theory is correct, it is fascinating to consider the weather conditions the Vikings faced. Reflecting on their adaptability and survival techniques offers valuable insights into how they may have remained in Greenland much longer than previously believed.





Related Trips
Blog



Polar Bear Sets Impressive New Diving Record

Not Eskimos: 10 Enlightening Facts About the Inuit

Greenlandic Inuit Beliefs

The Impact of Small vs. Large Cruise Ships
First to the North Pole: Five Failed but Brave Expeditions

How Arctic Wildlife Differs from Antarctic

The Eight Albatrosses of Antarctica and the Sub-Antarctic

Albatross, penguin and krill research in Antarctica

The Plants of Antarctica

Everything you need to know about Antarctic icebergs

A Day of Whale Watching in Antarctica

What the ice reveals about Antarctica

Deep Sea Dwellers: 10 Facts about The Antarctic Giant Isopod

9 Facts about the Greenland Shark

The South Georgia Seven: Hikes, Fjords, Whales, & Penguins

The Small but Social Commerson’s Dolphin

The secrets of Antarctic seals revealed

5 Life Lessons You'll Learn in Antarctica

12 Tips to Help Keep Birds Safe During an Antarctic Cruise






 20 Days / 19 Nights
20 Days / 19 Nights

